Vyux Rf
Depends on context In mathematics, Y is often used to represent the vertical axis of a graph In this context, f(x) is a function that takes a parameter x and returns a value A function is similar to a series of steps You give it a number and i.

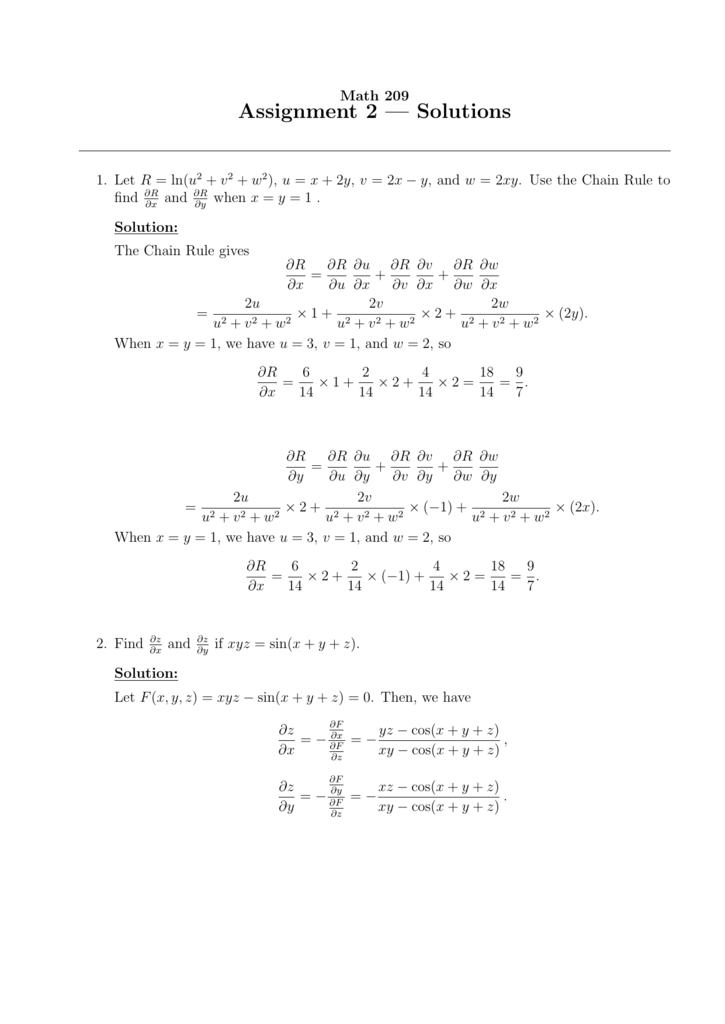
Vyux rf. Suppose that f = u iv is a complexvalued function which is differentiable as a function f R 2 → R 2 Then Goursat's theorem asserts that f is analytic in an open complex domain Ω if and only if it satisfies the Cauchy–Riemann equation in the domain (Rudin 1966, Theorem 112) In particular, continuous differentiability of f need not be assumed (Dieudonné 1969, §910, Ex 1) The. This video is intended to show how to graph the parent functions when a constant, v, is added to the functionThis is a thorough 15 minute discussion designe. Putting gives which can happen if either or Note that the function which is identically zero satisfies the functional equation If is not this function, ie, if for at least one value of , then plugging that value of (say ) into the equation gives Also, for any , the equation forces as well Further, so for all.
First 100 trials done by program just incase you wanted to see the results gives x then f(x) then whether or not f(x) was prime Furthermore ignore first two tests my algorithm works but not for first 100 trials done by program just incase you wanted to see the results gives x then f(x) then whether or not f(x) was prime Furthermore ignore first two tests my algorithm works but not for. Example 110 Let u = f(x/y), where f is an arbitrary (twice differentiable, with continuous second derivative) function of one variable Show that xux yuy = 0, and deduce that x2u xx 2xyuxy y 2u yy = 0 5 Solution Using the chain rule, we have, ux = f0 µ x y ¶ ∂ ∂x µ x y ¶ = 1 y f0 µ x y ¶, uy = f0 µ x y ¶ ∂ ∂y µ x y ¶ = − x y2 f0 µ x y ¶ So, xux yuy = x 1 y f0. S a d n e s s a s f x c k Entertainment Website Post de apreciación Art ∆Stylinson∆ Writer H A T E 討厭 Blogger Memes color petroleo ゾト羽 Entertainment Website E S Q U I Z O F R E N l A Personal Blog F U C K Teens & Kids Website 𝙍𝘼𝙏𝙏𝙄𝙋𝙎 Society & Culture Website A l t e r n a t i v e Interest Adolescentes Photography Videography —Felings.
W v ^ R g R g S v W ^ u V g e S n R X R g j } Y R G R g R. R C Cowsik 1, A Kłopotowski 1,2 & M G Nadkarni 1,3 Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences Mathematical Sciences volume 109, pages 57 – 64 (1999)Cite this article 65 Accesses 16 Citations Metrics details Abstract LetX andY be arbitrary nonempty sets and letS a nonempty subset ofX ×Y We give necessary and sufficient. R f (x;y)dA xy = ZZ S f (x(u;v);y(u;v)) @(x;y) @(u;v) dA uv Jason Aran Change of Variables & Jacobian June 3, 15 17 / Comments on the theorem Notice that when we apply the theorem, we convert 1 The function 2 The di erential 3 The limits of integration We typically apply the theorem if 1 The region over which we are integrating is particularly di cult 2 The function we are.
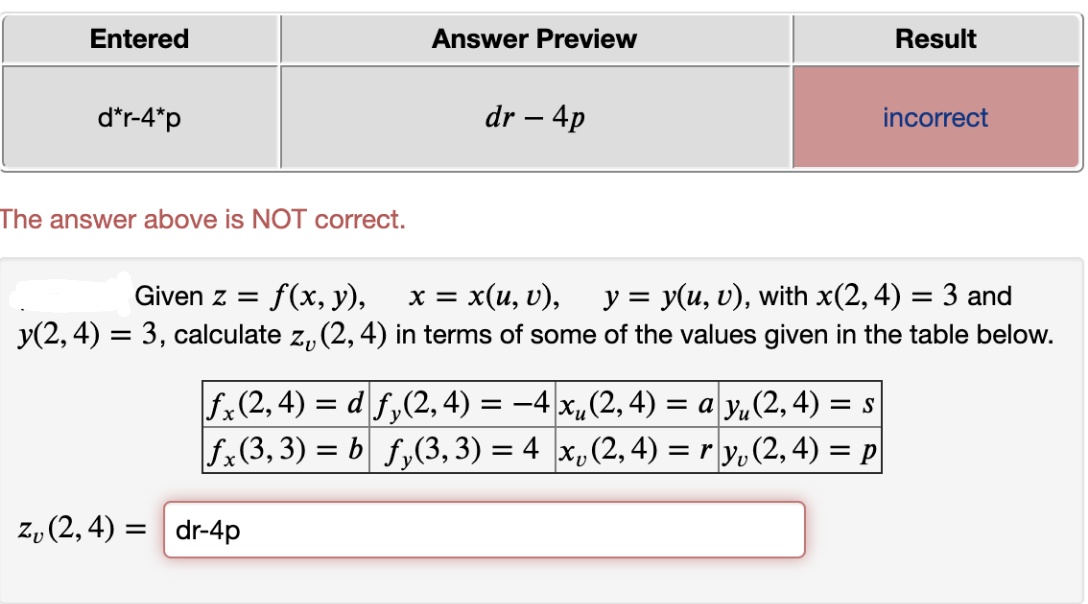
Input Geometric figure 3D plot Show contour lines;. Given z=f(x,y), x=x(u,v), y=y(u,v) , with x(1,2)=3 and y(1,2)=1 calculate zu(1,2) in terms of some of the values given in the table below fx(1,2)=1 fy(1,2)=s xu(1,2)=c yu(1,2)=a fx(3,1)=5 fy(3,1)=−2 xv(1,2)=r yv(1,2)=q zu(1,2)= Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) Previous question Next question Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculator. 08/04/13 · Suppose satisfies What can we say about ?.
Using the substitutions x = v x = v and y = u v, y = u v, evaluate the integral ∬ R y sin (y 2 − x) d A ∬ R y sin (y 2 − x) d A where R R is the region bounded by the lines y = x, x = 2, and y = 0 y = x, x = 2, and y = 0 Change of Variables for Triple Integrals Changing variables in triple integrals works in exactly the same way Cylindrical and spherical coordinate. D = 9 v 2 b q ' ´ \ r X Q v h b q A ^ y ¬ ) ` q O Z Æ W r X Q v r X Æ ` ² Ì f q Ø \ { s § O d } 2 8 ` f q Ø X d y r h y Î v z t Q i U b Z U ( O b d } ç F Ö Å ¢ ³ Ñ · Q c x F è Ï 92/2 ¤ Ô ¥ G ± ¨ ü ¦. X u x y p y u v x u u e τ ρ where pe is the pressure at the edge of the boundary layer andτ=µ∂u ∂y a) Assuming the flow outside of the boundary layer is inviscid, irrotational flow such that Bernoulli’s equation holds, show that Equation (A) can be manipulated to (C) 1 x y u u y u v x.
X v yu y (128) Now if f(z) is analytic in a region Rthen the CR equations hold there, u x= v yand u y= −v x, and (128) becomes dy dx u=const × dy dx v=const = −1 (129) The final result is that in regions of analyticity curves of constantuand curves of constant vare always orthogonal 2 Mappings 21 Conformal mappings y x R v u R∗ A complex mapping w= f(z) maps a region Rin the. Recall the definition of differentiation for a real function f(x) f0(x) = lim δx→0 f(xδx)−f(x) δx In this definition, it is important that the limit is the same whichever direction we approach from Consider x at x = 0 for example;. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Log in Angela G Numerade Educator Like Report Jump To Question Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4. R is called odd if f( x) = f(x) for all x 2R Let U e denote the set of realvalued even functions on R and let U o denote the set of realvalued odd functions on R Show that RR = U e U o Proof 1 First, we check that U e and U o are. But clearly this is true set theoretically (if u 2W 1 and u 2W 2, then of course u 2W 1\W 2), ie W 1 \W 2 is the largest subset of V contained in both W 1 and W 2Since we have shown in the lectures that W 1 \W 2 is also a subspace, we are done 3 Let W 1 and W 2 be subspaces of a vector space V Show that the following statements are equivalent (i) W 1 \W 2 = f0g (ii) If w.
R X fgd j kgkp def of ’(f)(g) sup g2Lp;g6=0 kfgk1 kgkp j Z fgj Z jfgj sup g2Lp;g6=0 kfkq H older Hence k’(f)k kfk For k’(f)k kfk, use the fact that k’(f)k is de ned as a supremum k’(f)k is the smallest number such that k’(f)(g)k k’(f)k kgk holds for all g(6= 0) In other words, if we can nd a gfor which k’(f)(g)k kgk kfk, then k’(f)k = supg2Lp;g6=0 n k’(f)(g)k kgk o kfk. 15 ∫∫ R (x – 3y) dA, where R is the triangular region with vertices (0, 0), (2, 1), and (1,2);. ~r(u,v) = hx(u,v),y(u,v),z(u,v)i It is given by three functions x(u,v),y(u,v),z(u,v) of two variables Because two parameters u and v are involved, the map ~r is often called uvmap If we keep the first parameter u constant, then v → ~r(u,v) is a curve on the surface Similarly, if v is constant, then u → ~r(u,v) traces a curve the surface These curves are called grid curves This can.
Using the CauchyRiemann equations, show that if f and f are both holomorphic then f is a constant Solution Let f = uiv,so f = u iv Since they are holomorphic, we can use the CauchyRiemann equations ux = vy and ux = vy) ux = vy = 0 uy = vx and uy = vx) uy = vx = 0 Therefore ux = uy = 0so uis constant, and similarly vx = vy = 0so v is. $$ \frac{\partial}{\partial r} v(x(r,\theta),y(r,\theta)) = \frac{\partial v}{\partial x}\frac{\partial x}{\partial r} \frac{\partial v}{\partial y}\frac{\partial y}{\partial r}, $$ which can be equivalently expressed as $$ v_r = v_xx_r v_yy_r$$ Try and use the above information and come back with whatever (if any) issues you have share cite improve this answer follow edited Jun. Factor $$ 4(xy)t(xy) $$ 0016 View Full Video Already have an account?.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Reno, NV 557 Email Qipingataolcom Website wwwcseunredu/~yanq I came to the US. In this *improvised* video, I show that if is a function such that f(xy) = f(x)f(y) and f'(0) exists, then f must either be e^(cx) or the zero function It'. X = 2u v, y = u 2v check_circle Expert Solution Want to see the full answer?.
Question Given Z = F(x,y), R = X(u, V), Y=y(u, V), With X(6,2) = 5 And Y(6,2) = 1, Calculate Zu(6,2) In Terms Of Some Of The Values Given In The Table Below Fa(6,2) = B Fy(6,2) = Czu(6,2) = A Yu(6,2) =p F=(5, 1) = 1 Fy(5, 1) = 2 X,(6,2) = Syv(6,2)=r Zu(6,2) = This problem has been solved!. X = rcosθ, y = rsinθ Changing the integral to. M f (x(u,v), y(u,v),z(u,v)) r u (u,v) r v (u,v)dudv r Dr Hempel – Mathematische Grundlagen Oberflächenintegral 11 Fluß durch eine Fläche Wir wollen die betrachtete Fläche wie schon bisher durch den Normalenvektor n(x, y, z) r charakterisieren Ein solcher Normalenvektor sollte in jedem Punkt der Fläche definiert sein Wird nun diese Fläche S von einem Vektorfeld (zB einer.
Contour plot Alternate form assuming x and y are real Alternate form Properties as a function Domain Range Parity Partial derivatives Stepbystep solution;. If we approach from the right (δx → 0) then the limit is 1, whereas if we approach from the left (δx → 0−) the limit is −1 Because these. If f is injective, then X = f −1 (f(X)), and if f is surjective, then f(f −1 (Y)) = Y For every function h X → Y, one can define a surjection H X → h(X) x → h(x) and an injection I h(X) → Y y → y It follows that = This decomposition is unique up to isomorphism Category theory In the category of sets, injections, surjections, and bijections correspond precisely to.
Y= y z= f(x;y) For example, the plane 3x 2y z= 6 can be parametrized as x= x;. Experts are waiting 24/7 to provide stepby. Y= y z= 6 3x 2y Note that the given equation also implies that 2y= 6 3x zso that y= 3 3 2 x 1 2 zSo.
Rodan Fields Gives You the Best Skin of Your Life and the Confidence That Comes with It Created By StanfordTrained Dermatologists, We Understand Skincare. For = /2, x 0, 0 y y v y u i dz df (2) And both results must be the same y v x u , y u x v (CauchyRiemann condition) or x y x y v u u v The CauchyRiemann conditions are necessary for the existence of a derivative of f (z) If df /dz exists, the CauchyRiemann conditions must hold Conversely, if the CauchyRiemann conditions are satisfied and the partial derivatives of u and v. F(x;y)dxdy = ZZ D⁄ f(x(u;v);y(u;v)) fl fl fl fl @(x;y) @(u;v) fl fl fl fldudv We proved this for a linear map if f =1 when it says that the area of D is the area of D⁄ times the Jacobian determinant which is the determinant of the linear map The general case follows by dividing up D⁄ into smaller sets on which we can approximate the map by its linearization If (u;v) is close.
Surface 2 u;v ~r(u;v) = hx(u;v);y(u;v);z(u;v)i Examples 1If a surface is given by a formula z= f(x;y);it can be parametrized by taking xand yto be two parameters and considering the parametric equations x= x;. Indefinite integral assuming all variables are real Download Page POWERED BY THE WOLFRAM. 01/02/1999 · When isf(x,y) = u(x) v(y)?.
28/01/ · Example 42 Let R be a relation on the set A of ordered pairs of positive integers defined by (x, y) R (u, v) if and only if xv = yu Show that R is an equivalence relation If (x, y) R (u, v) , then xv = yu Check Reflexive If (x, y) R (x, y), then xy = yx Since, xy = yx Hence , R is. FHunt @ 1921 A X R b g T13F @ Polymestor @ R SDonoghue Ede Mestre @ 19 A X R b g T13F @ All Prince @ R FFox RDay @ 1919 A X R b g T13F @ Dominion @ R ASmith FBarling @ 1915 N `1918 N @ ~ 1914 A X R b g T13F @ Marten @ R FRickaby FDalring @ 1913 A X R b g T13F @ Louvois @ R WSaxby DWaugh @ 1912 A X R b g T13F @ Catmi. R f(x,y)dA = Z Z R g(r,θ)rdrdθ This involves introducing the new variables r and θ, together with the equations relating them to x,y in both the forward and backward directions (2) r = p x2 y2, θ = tan−1(y/x);.
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If u = f(r) , where r^2 = x^2 y^2 z^2 , then prove that ∂^2u∂x^2 ∂^2u∂y^2 ∂^2u∂z^2 = f^\" (r) 2rf (r). Exercise 1C24 A function f R !. See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Previous question Next question.
R is called even if f( x) = f(x) for all x 2R A function f R !. Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. This new website will come out of the beta phase soon we hope to be fully operational sometime after Christmas, at which point the old website will be archived and closed The new site will continue to be tested and improved.
Search the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking for. X iy the function f can also be thought of as a function from R2 to R From this point of view the function f can also be written as f(x,y) = x2 y2 Since the partial derivatives of f are continuous throughout R2 it follows that f is differentiable everywhere on R2 But what happens if we now view f as a function on C and think. Answer to Given z = f(x,y), x = x(u,v), y =y(u,v) , with x(2,2) =1, y(2,2)=4 , calculate z_u(2,2) in terms of some of the values.
Therefore, the curve x 22xyy = 2 becomes 2u 2v2 = 2, which is equivalent to u v2 = 1 The integral is equal then to ZZ u2v2 1 (2u2 2v2) 4 p 3 dudv Passing to polar coordinates, we get that it is equal to 8 p 3 Z 2ˇ 0 Z 1 0 r2 rdrd = 8 p 3 2ˇ 1 4 = 4ˇ p 3 2R Find a function fsuch that rf= F for F = yi (x z) j yk Use it to nd. 0 0) 2→ R defined by, Φ(u,v) = (x(u,v),y(u,v)), Φ x = x(u,v) y = y(u,v) 6 Φ has Jacobian matrix, DΦ = ∂x ∂u ∂x ∂v ∂y ∂u ∂y ∂v Hence detDΦ 6= 0 at ( u 0,v 0), ie DΦ is nonsingular at (u 0,v 0) By the IFT there exists a neighborhood V of (u 0,v 0) such that W = Φ(V) is open in R2 R2 → W ⊂ R2 is a diffeomorphism, ie, Φ−1 W ⊂ R2 → V ⊂ R2 is. Let w= f(x;y;z) be a function of three variables Introduce a new object, called thetotal di erential df= f xdx f ydy f zdz Formally behaves similarly to how fbehaves, fˇf x x f y y f z z However it is a new object (it is not the same as a small change in fas the book would claim), with its own rules of manipulation For us, the main use of the total di erential will be to understand.
Check out a sample textbook solution See solution arrow_back Chapter 159, Problem 14E Chapter 159, Problem 16E arrow_forward Want to see this answer and more?. Answer to Use the given transformation to evaluate the integral int int_{R} (x 10y) dA where R is the triangular region with vertices. 14/12/10 · Express f(x,y,z) = yz in terms of u and v and evaluate \\int\\int_S f(x,y,z)dS This is supposed to be simple but I really don't know how to do this I rewrote f(x,y,z) = yz as x = g(y,z) so then \\Phi(y,z) = (y,z, x) Tx = (0,0,1) and Ty=(1,0,0) and their corss product, n, is Am I even.

Solved 1 If F S Is A Differentiable Function Show That Chegg Com

Solved 1 Draw The Tree Diagram For The Chainrule And Wr Chegg Com

A A Q W E R T Y U I O P A S D F G H J K L Z X C V B N M
Vyux Rf のギャラリー

Solved Consider The System Of Equations F U V X Y Z Chegg Com

Graph Of F R S N X Y U V N 10 U 0 3 V 0 6 R 3 S 2 Download Scientific Diagram

Obfuscated Hello World Program

Solved Given Z F X Y X X U V Y Y U V With Chegg Com

Commutators Of Higher Order Riesz Transform Associated With Schrodinger Operators Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub

Calculus Iii

1 5 Pts True Or False A Let R Denote A Plane Region And U V U X Y V X Y Be A Homeworklib

You Should Be Able To Solve Any Homework Tutorial Problem The Very Similar To Them The Formulae Below Will Be Appended
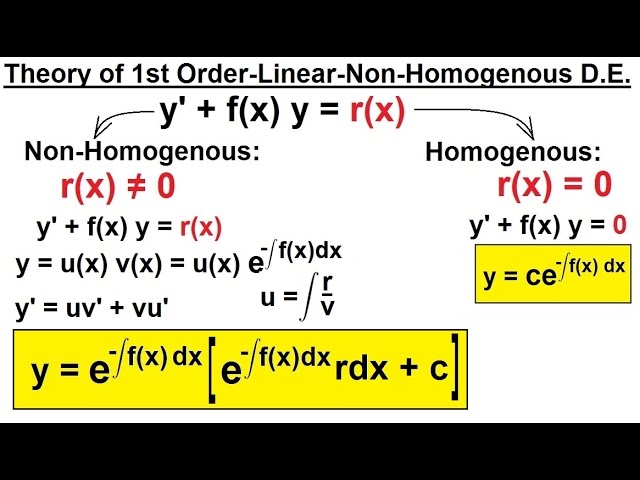
Differential Equation 1st Order Linear Variation Of Parameters 1 Of 4 Theory Youtube
Transactions U M 1 T 1 Vt 1 1 7 R Vvin V F T R S If V 4 F

Can Someone Advise Me On Problem 48 Please Calculus

Solved Problem 2 Use The Chain Rule Case Ii To Find 02 A Chegg Com

Solved 1 Point Given Z F X Y X X U V Y Y U Chegg Com

Orthogonal Families Of Curves

1 Vytah

U Unit3 Vm

Consider The Following Relations From A To B Where Br A U V
Solved Which Of The Following Subsets Of R3 Are Subspaces Of R3 Course Hero

Consider A Transformation T U V X U V Y U V From R 2 To R 2 Suppose T Is A Linear Transformation T U V Au Bv Cu Dv Then The Derivative Ppt

Consider A Transformation Tu V Xu V Yu
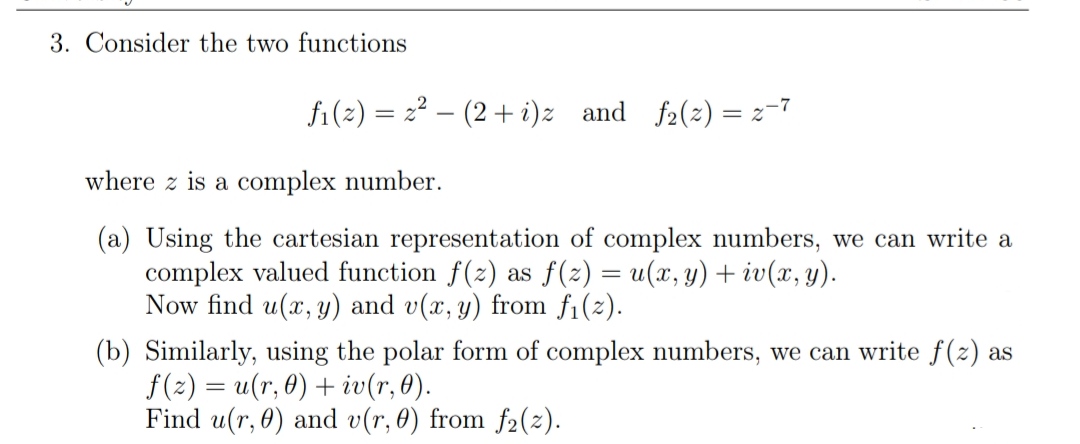
Answered 3 Consider The Two Functions Fi 2 Bartleby

The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example 1 Page 152 Illustrates The Quotient Rule Reca

Hw2sol

Complex This Class Requires Heavy Notes This Will Help To Get Ahead In The Game Very Studocu

2 Functional Dependence Differential Calculus Functions And Mappings

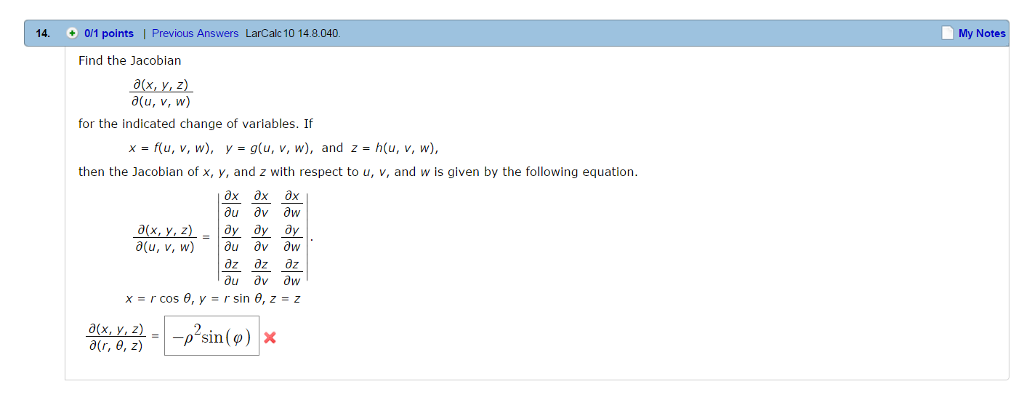
Solved 9 The Jacobian In Order To Change The Variables Chegg Com

Solved Problem 1 Separation Of Variables Can Be Applied Chegg Com

Find F Z U X Y Iv X Y With U Or V As Given Check By The Cauchy Riemann Equations For Analyticity U Xy Homework Help And Answers Slader

Pdf Homework 1 9 8 9 9 Sojun Yun Academia Edu

Gec2 Tutorials Functions Of Several Variables
Defter I Kutubhne I Ayfya O Nv T Y T Vovvoa Vo Xaa J 4 Ji Y Ije I Y F Van Vy Nn Y A J V R R Yvy

Help To Clarify Proof Of Euler S Theorem On Homogenous Equations Mathematics Stack Exchange

Surface Integrals With Parameterized Surface Part 1 Youtube
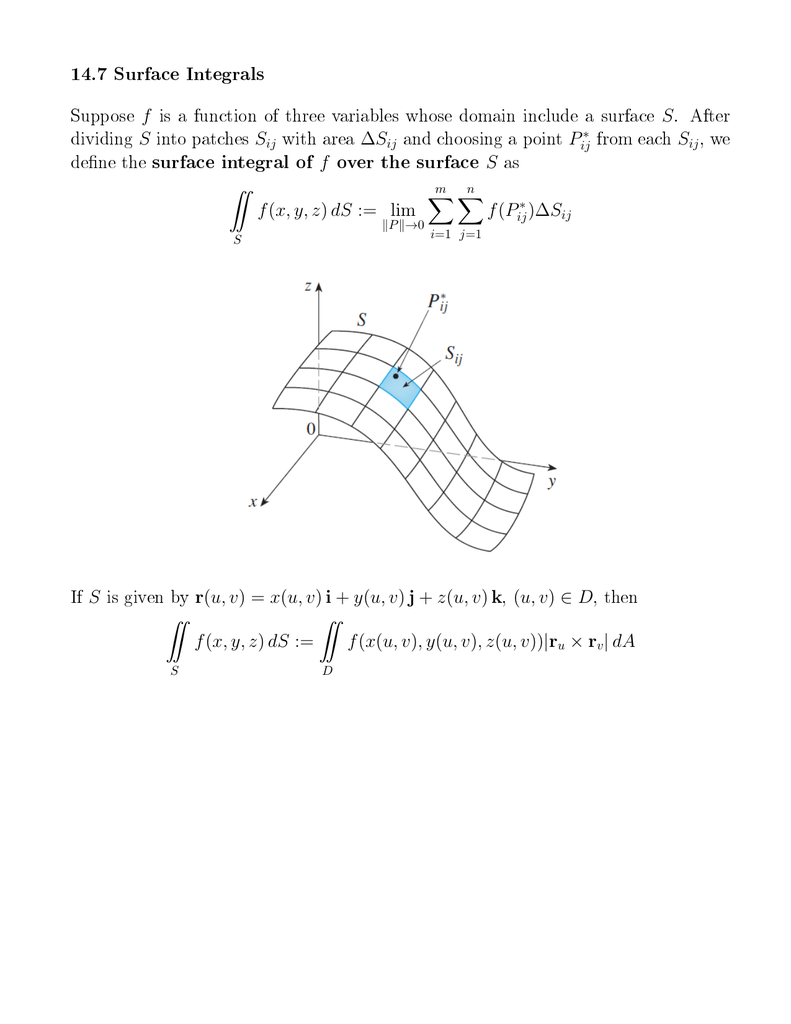
14 7 Surface Integrals
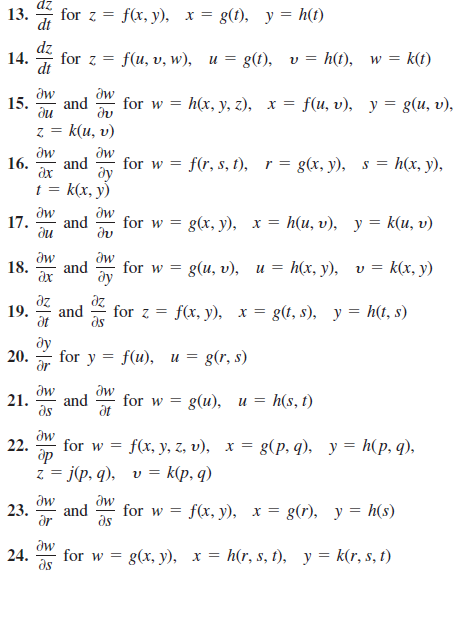
Answered For Z 13 Dt F X Y X G T Y Bartleby

Formulas For Exam 2

Ph D Comprehensive Examination Partial Differential Equations

2 Functional Dependence Differential Calculus Functions And Mappings
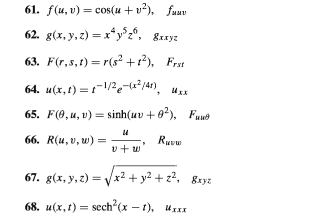
Answered 61 F U V Cos U V Fuuv 62 Bartleby

U Unit3 Vm

Pdf The Cauchy Problem For A Second Order Nonlinear Hyperbolic Equation With Initial Data On A Line Of Parabolicity
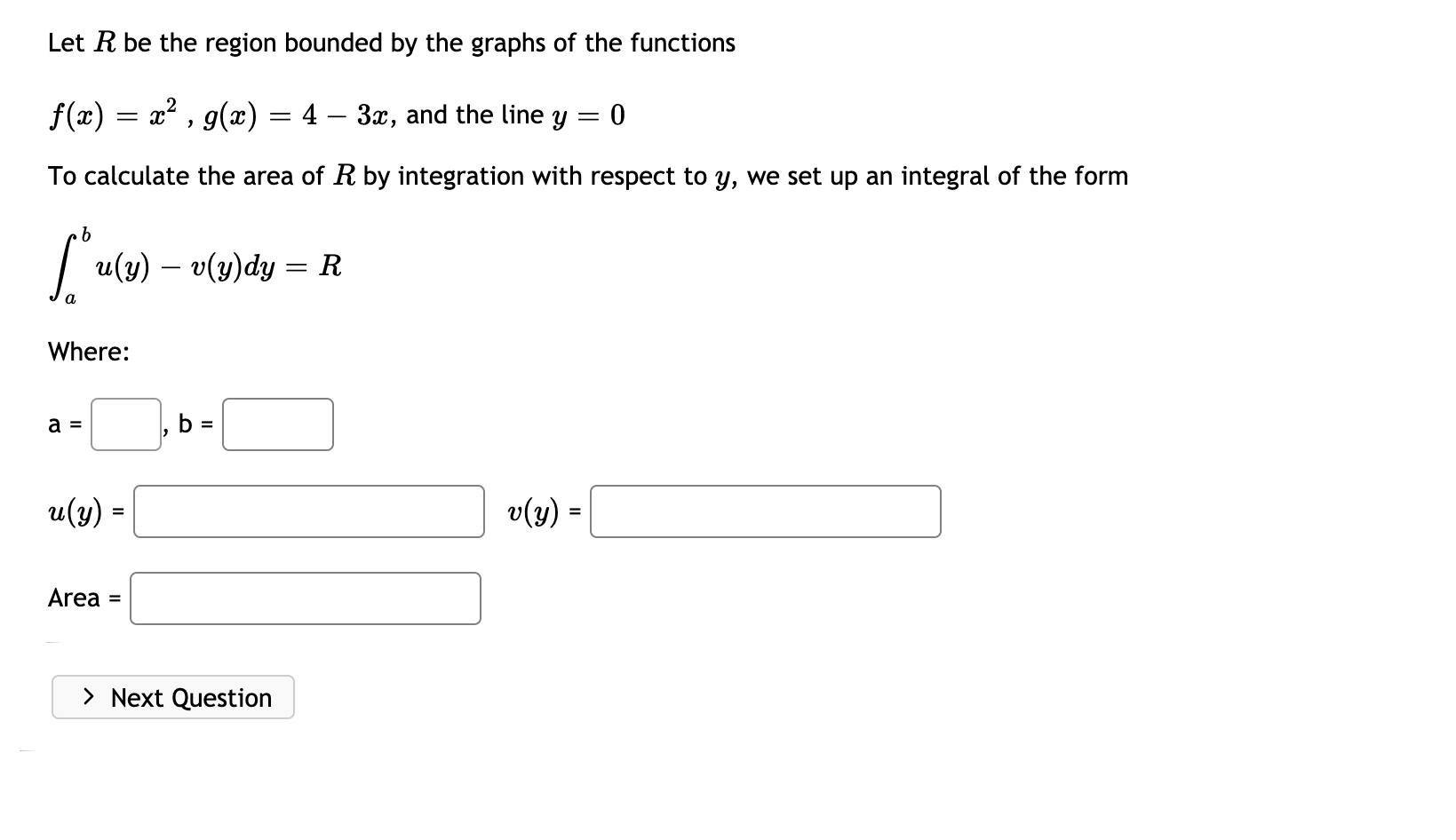
Answered Let R Be The Region Bounded By The Bartleby

Solved 1 Suppose That V Is A Harmonic Conjugate Of U In Chegg Com

Let X And Y Be Independent Exponential Random Variables With Pa Rameter 1 Given Homeworklib
Answered F X Y X I V Y 2 4 3 Bartleby
Let U X And V X Satisfy The Differential Equations Du Dx P X U F X And Dv Dx P X V G X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Document
Assignment 2 Solutions

Solved 18 W X Y Z 19 T F P Q R R R X Y Z Chegg Com

Solved Let F U V U V Uv 2 And U U X Y E X Chegg Com
Solved Find The Jacobian Partial Differential X Y Z P Chegg Com

A B F G J M Q R T U X Gymnomitrion Parvitextum C E H I Download Scientific Diagram
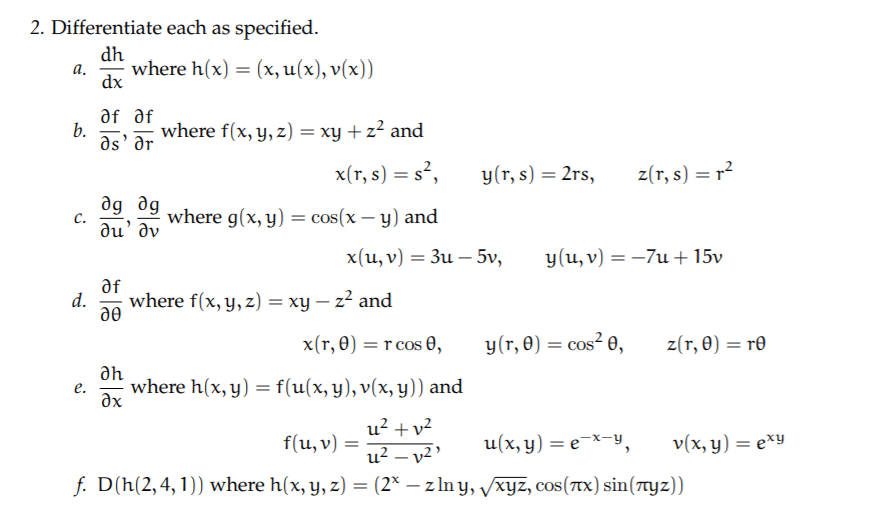
Solved C 2 Differentiate Each As Specified Dh Where H Chegg Com

Ug Math

Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu

The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example Ppt Download

Ab2 5 Surfaces And Surface Integrals Divergence Theorem Of Gauss Pdf Free Download

Maths Trigonometric Functions Cartesian Coordinate System

Real Analysis Problem Is Attached In The Picture Please Only Attempt If You Re Familiar With The Homeworklib

C2 14 2 Con Pauta Docsity
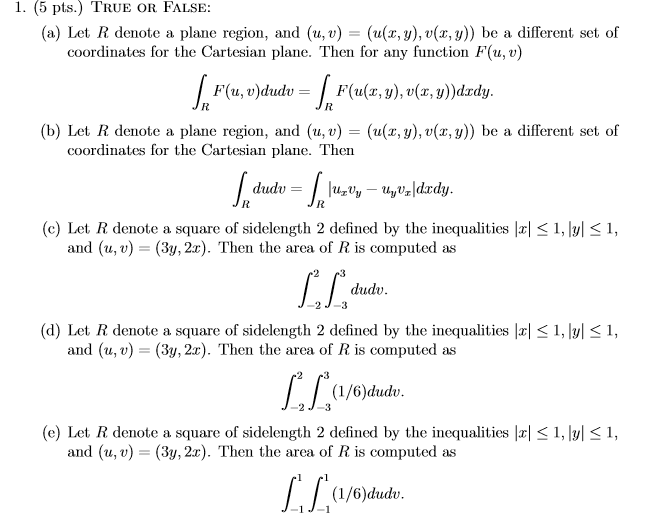
Solved 1 5 Pts True Or False A Let R Denote A Plane Chegg Com

Formulas For Exam 3

Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu

Get Answer Help Anyone Please Solves This I Still Cant Figure It Out Why Transtutors
Differential Equation 1st Order Linear Variation Of Parameters 1 Of 4 Theory Youtube

U Unit3 Vm




