K Pxx X
• For p > n, lim x→∞ xp−n = ∞, then lim x→∞ ex xn = ∞ Quiz Quiz 1 domain of ln 1x2 (a) x > 1, (b) x > −1, (c) any x 2 domain of ln x p 4x2 (a) x 6= 0, (b) x > 0, (c) any x 2 Differentiation and.

K pxx x. (x) in mind in the rst place, and took the inner product in ’s space instead) Remember the optimization problem for SVM?. Proof Let x be a real number in the range given, namely x > 1 We will prove by induction that for any positive integer n, (1 x)n 1 nx holds for any n 2Z Base case For n = 1, the left and right sides of are both 1 x, so holds Induction step Let k 2Z be given and suppose is true for n = k We have (1 x)k1 = (1 x)k(1 x) (1. 2 = k)P(X 2 = kX 0 = i) = XN k=1 p kj P2 ik = (P3) ij 157 The threestep transition probabilities are therefore given by the matrix P3 P(X 3 = j X 0 = i) = P(X n3 = j X n = i) = P3 ij for any n General case tstep transitions The above working extends to show that the tstep transition probabilities are given by the matrix Pt for any t P(X.
P(X = 1) = 4!1!3!. Logistic Regression Fitting Logistic Regression Models I Criteria find parameters that maximize the conditional likelihood of G given X using the training data I Denote p k(x i;θ) = Pr(G = k X = x i;θ) I Given the first input x 1, the posterior probability of its class being g 1 is Pr(G = g 1 X = x 1) I Since samples in the training data set are independent, the. P k (1p) (nk) Like this (to 4 decimal places) P(X = 0) = 4!0!4!.
In this case n=4, p = P(Two) = 1/6 X is the Random Variable ‘Number of Twos from four throws’ Substitute x = 0 to 4 into the formula P(k out of n) = n!k!(nk)!. May 29, 18 · Transcript Ex 24, 3 Find the value of k, if x 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases (i) p(x) = x2 x k Finding remainder when x2 x k is divided by x 1 Step 1 Put Divisor = 0 x 1 = 0 x = 1 Step 2 Let p(x) = x2 x k Putting x = 1 p(1) = (1)2 1 k = 1 1 k = 2 k Thus, Remainder = p(1) = 2 k Since x 1 is a factor of x2 x k Remainder is zero, 2 k = 0 k. If P(x) had an irreducible cubic factor q(x) in kx, then P(x) = 0 would have a root in a cubic extension K of k Since K k = 3, the eld Khas p3 elements, and jK j= p3 1 By Lagrange, the order of any element of K is a divisor of p 3 1, but 7 divides neither 3 1 = 26 = 5 mod 7.
Theorem 36 Let F be any partition of the set S Define a relation on S by x R y iff there is a set in F which contains both x and y Then R is an equivalence relation and the equivalence classes of R are the sets of F Pf Since F is a partition, for each x in S there is one (and only one) set of F which contains x. Title Microsoft Word Installation Instruction Kodlin LoweringKit KEnglish Author JamesKodlin USA Created Date 2/23/21 PM. Ex = X∞ k=0 xk k!.
P(X Y ≤ 1) = Z 1 0 Z 1−x 0 4xydydx = 1 6 (b) Refer to the figure (lower left and lower right) To compute the cdf of Z = X Y, we use the definition of cdf, evaluating each case by double integrating the joint density over the subset of the support set corresponding to {(x,y) x y ≤ z}, for different cases. Binomial with n = and p = x P( X = x) 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 6 7 097 8 9 The corresponding graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function for the B(,1/6) distribution are shown below. Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange.
P(A B) = 03 f (x) probability density function (pdf) P(a ≤ x ≤ b) = ∫ f (x) dx F(x) cumulative distribution function (cdf) F(x) = P(X≤ x) μ population mean mean of population values μ = 10 E(X) expectation value expected value of random variable X E(X) = 10 E(X Y) conditional expectation expected value of random. P k(x) = X p k(n)xn = Yk i=1 1 1 xi = 1 (1 x)(1 x2) (1 xk) Taking the conjugate partition gives a bijection between partitions of nwith parts kand partitions of nwith at most kparts Therefore P k(x) also counts partitions with at most kparts (2) To count partitions with exactly kparts, we can again take conjugates and count partitions. ProofLet fK g 2A be a family of convex sets, and let K = \ 2AK Then, for any x;y2 K by de nition of the intersection of a family of sets, x;y2 K for all 2 nd each of these sets is convex Hence for any 2 A;and 2 0;1;(1 )x y2 K.
Max Xm i=1 i 1 2 Xm i;k=1 T i jy iy k x i x k inner product st 0 i C;i= 1;;mand Xm i=1 iy i= 0 You can replace this inner product with another one, without even knowing. Induction) The following approach is often called reservoir sampling Suppose we have a sequence of items passing by one at a time We want to maintain a sample of one item with the property that it is uniformly distributed over all the items that we have seen at each step. Lecture 15 Order Statistics Statistics 104 Colin Rundel March 14, 12 Section 46 Order Statistics Order Statistics Let X 1;X 2;X 3;X 4;X 5 be iid random variables with a distribution F with a range of (a;b) We can relabel these X’s such that their labels correspond.
V P Z } u v o } } o } v } Y µ } î X. P(Y a2) E(Y) a = Var(X) a2 But notice that the event Y a2 is the same as jX E(X)j a, so we conclude that P(jX E(X)j a) Var(X) a2 Chebyshev’s inequality gives a bound on the probability that X is far from it’s expected value If we set a= k˙, where ˙is the standard deviation, then the inequality takes the form P(jX )j k˙) Var(X) k 2. Xk i=1 1/p (since X i ∼ geom(p)) = k/p 5 (MU 218;.
X∞ k=n (1−p)kp = 1−p (1−p)n p so P(X ≤ n) = 1−(1−p)n If X is a geometrically distributed random variable with parameter p, then E(X) = X∞ n=1 n(1−p)n−1p = X∞ k=0 (k 1)(1−p)kp = p X∞ (k 1)(1−p)k Using the notes above E(X) = p X∞ k=0 (k 1)(1−p)k = p 1 1−(1−p)2 = p 1 p2 so E(X) = 1 p Also E(X2) = X∞ n=1. Periodic extension of X (k) Furthermore, because of the symmetry imposed on X (k) the value X (0) is constrained to be zero (see Problem 93 below) A corrected version is shown at the top of page 93 The second figure requiring correction is the viewgraph used to illustrate circular convolution On that figure x2((m))N is incorrectly drawn. = n k · λ1 λ1 λ2 k · λ2 λ1 λ2 n−k Hence the conditional distribution of X given X Y = n is a binomial distribution with parameters n and λ1 λ1λ2 E(XX.
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable, denoted or , is a generalization of the weighted average, and is intuitively the arithmetic mean of a large number of independent realizations of The expected value is also known as the expectation, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first momentExpected value is a key concept in economics, finance, and many. î X K^ Z'K^ î X í X K P } v _ À o u } U } r µ } µ } P } U À P u o } v } !. X d J N J K e P N f ` LK f b LK f J K b I c N I b _ g ^ e W018MS0006O Submission Type Official Approval Date11/29/18 Superseded SPA ID WA.
E−(λ1λ2) · (λ1λ2) n n!. The norm k·k2 is induced by the inner product hg,hi = Z 1 −1 g(x)h(x)dx Therefore kf −pk2 is minimal if p is the orthogonal projection of the function f on the subspace P3 of quadratic polynomials Suppose that p0,p1,p2 is an orthogonal basis for P3Then p(x) = hf,p0i hp0,p0i p0(x) hf,p1i hp1,p1i p1(x) hf,p2i hp2,p2i p2(x). Share your videos with friends, family, and the world.
·e −λ2 · λ n−k 2 (n−k)!. Title CongregateFacilitiesGroupA_GroupB_Guidance_321xlsx Author CarrieRice Created Date 3/19/21 AM. K P X 1,387 likes @memeiraporamor.
Write the function in the form f(x)=(xk)q(x)r for the given value of k Use the remainder theorem and synthetic division to find the value of the function Factor the polynomial completely using synthetic division given one solution Verify the given factors of the function and find the remaining factors of the function. PXZ=n(k) = P(X = k,Z = n) P(Z = n) = P(X = k)P(Y = n−k) P(Z = n) = e−λ1 · λ k 1 k!. P(jX 2EXj t˙) = P(jX EXj2 t2˙) E(jX 2EXj) t 2˙ = 1 t2 3 Cherno Method There are several re nements to the Chebyshev inequality One simple one that is sometimes useful is to observe that if the random variable Xhas a nite kth central moment then we have that, P(jX EXj t) EjX EXjk tk.
Simple and best practice solution for x(4k)=p equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,. Title Microsoft Word Detailed Advertisement (Professor) Author admin Created Date 11/24/ PM. ^ Z lE v i K v P >> X t v Ç } À P o } Z } P v o } Á v v } Z } P v o o ( r Z o X K µ µ } u ^ À ^ o o } À o o í r ô ó ó r ò ð ò r ñ î ô ô }.
× (1/6) 1 (5/6) 3 = 4 × (1/6) × (5/6) 3. Expected Value and Standard Dev Expected Value of a random variable is the mean of its probability distribution If P(X=x1)=p1, P(X=x2)=p2, n P(X=xn)=pn E(X) =. × (1/6) 0 (5/6) 4 = 1 × 1 × (5/6) 4 = 043;.
= 1 x 1 x2 1·2 x3 1·2·3 ··· • For large x > 0, ex > x p p!. K p(x k) Interpretations (i) The expected value measures the center of the probability distribution center of mass (ii) Long term frequency (law of large numbers we’ll get to this soon) Expectations can be used to describe the potential gains and losses from games. X h } Z µ P v } v r µ P v À v } v } P Z X K u Ì v } v r µ P Z Ç J x / v µ µ } µ } v P P Ç U v P Á Z o } Á } } o } v P } v P v À o U Á Á Á XZ Æ& o X W, ZD K>K'/ >^ t EKE rKW/K.
YingweiWang MethodsOfAppliedMathematics On the other hand, kx0 − y0k ≤ ky0 −y n k kky n k −x0k → d, as k → ∞ So y0 is just what we want to find 2 Lineartransformation Question Find the norm of the operator A ∈ B(X) given by (Af)(t) = tf(t), 0 ≤ t ≤ 1,. X ∼ geom(p) Note in passing that P(X > k) = (1−p)k, k ≥ 0 Remark 13 As a variation on the geometric, if we change X to denote the number of failures before the first success, and denote this by Y, then (since the first flip might be a success yielding no failures at all), the pmf becomes p(k) = ˆ p(1−p)k, if k ≥ 0;. To prove (3), note that ifm(X)=h(X)k(X) withdeg h anddeg k lessthandeg m , theneither h ( α )=0or k ( α )=0, sothatby(1), either h ( X )or k ( X )isamultipleof m ( X ),whichisimpossible.
(b) Using the result of problem (a), prove that if f (x) = ex and Pn(x) is the interpolating polynomial of order n defined at the n1 regularly spaced nodes x k =. A Markov chain is a stochastic process, but it differs from a general stochastic process in that a Markov chain must be "memoryless"That is, (the probability of) future actions are not dependent upon the steps that led up to the present state This is called the Markov propertyWhile the theory of Markov chains is important precisely because so many "everyday" processes satisfy the. Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange.
3 Now we prove that if U is uniformly distributed over the interval (0,1), then X = F−1 X (U) has cumulative distribution function F X(x)The proof is straightforward P(X ≤ x) = PF−1 X (U) ≤ x = PU ≤ F X(x) = F X(x) Note that discontinuities of F become converted into flat stretches of F−1 and flat stretches of F into discontinuities of F−1. 219k Followers, 600 Following, 173 Posts See Instagram photos and videos from P H E N I X (@thisisphenix). KXP is an electronic rock band from Helsinki, Finland The band consists of Timo Kaukolampi, Tomi Leppänen, Anssi Nykänen, and Tuomo Puranen For their second album II.
Of course, a binomial variable X is not distributed exactly normal because X is not continuous, eg you cannot get 37 heads when tossing 4 coins In the binomial, P(X ≤ a) P(X ≥ a 1) = 1 whenever a is an integer But if we sum the area under the normal curve. ⇒ ex xn > x −n p!.

Deriving The Variance Of The Difference Of Random Variables Video Khan Academy
Find The Values Of A And B If The Function F Defined By F X X 2 3x A X 1 And Bx 2 X 1 Is Differentiable
If P X X2 4x 3 Then Evaluate P 2 P 1 P 1 2 Studyrankersonline
K Pxx X のギャラリー

Sma8 Ljg7tlrm

Problem 1 5 Points Polynomial Conjecture Let Chegg Com

Find The Relationship Between A And B So That The Function F Defined By F X Ax 1 If X3 Is Continuous At X 3
A Delightful Site For Writers And Lovers Of Words And Language It Is All About The Number Zero Its Place In The History Philosophy And World Literatures We Have Heard Of Calling Someone A Total Zero As An Insult But What Does Zero Really Mean This

Integrals Cheat Sheet Pauls Online Math Notes
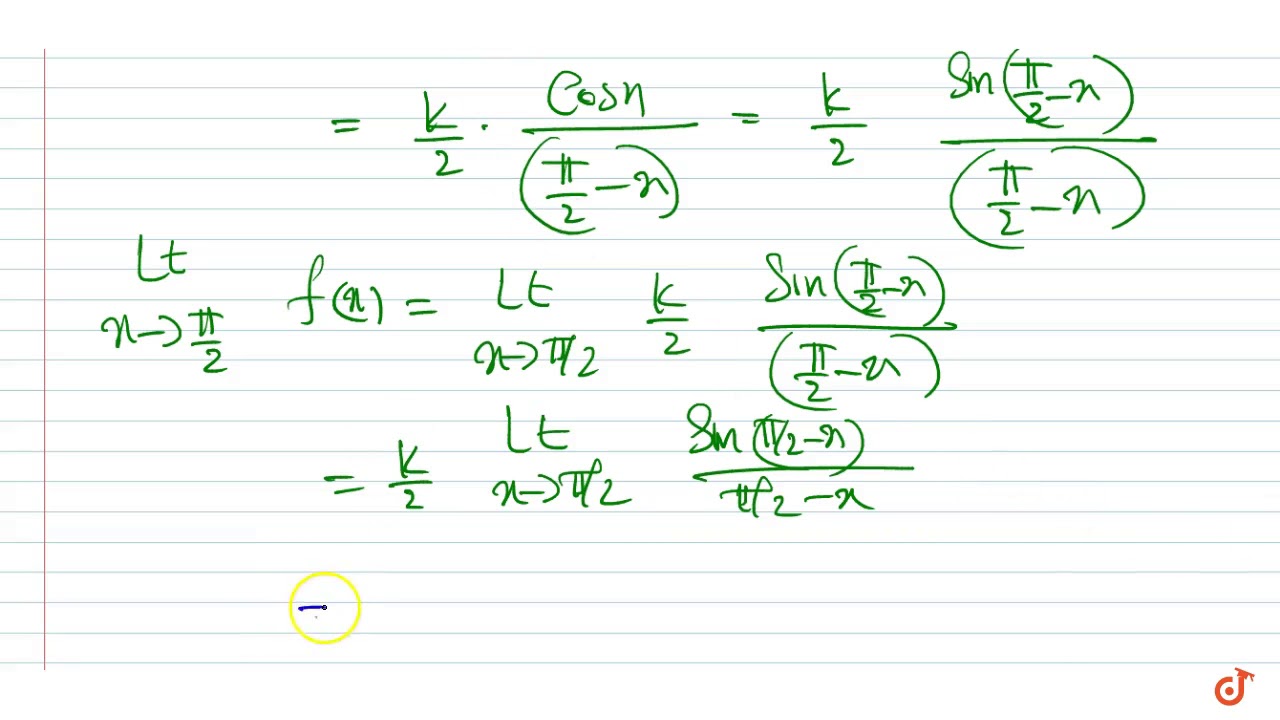
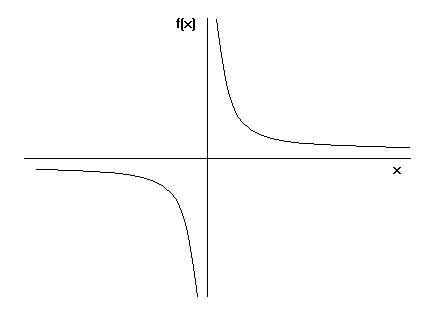
For F X Kcosx Pi 2x If X Pi 2 3 If X Pi 2 Then Find The Value Of K So That Youtube

Worked Example Point Where A Function Isn T Continuous Video Khan Academy

Normal Distribution Wikipedia
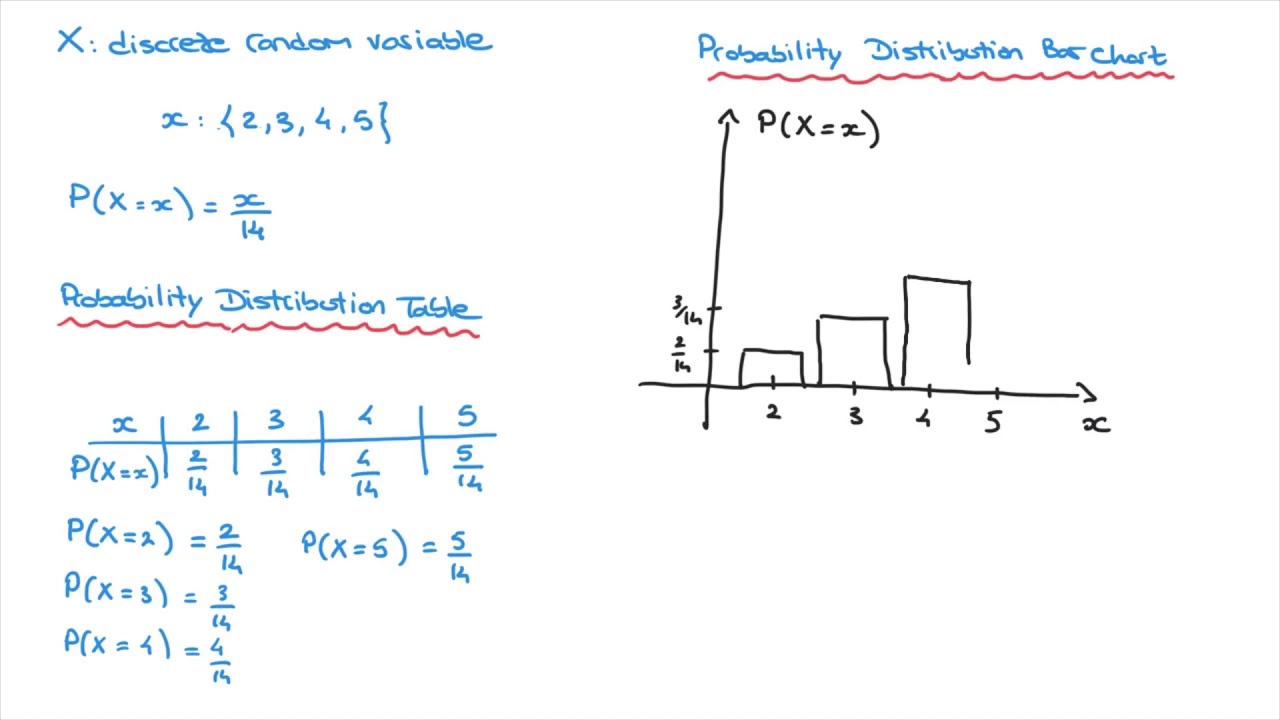
Discrete Random Variables Probability Distribution Functions

Show That The Function F X X Sin 1 X When X 0 0 When X 0 Is Continuous Butnot Diff Youtube
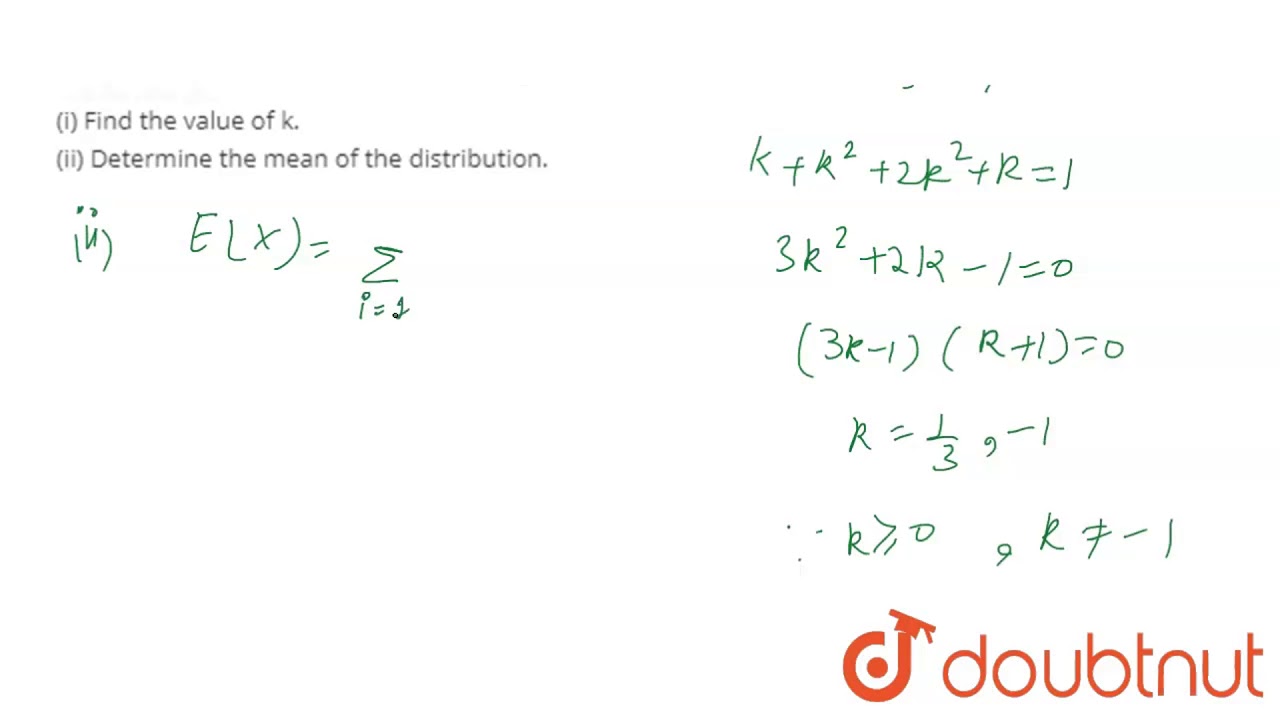
A Discrete Random Variable X Has The Probability Distribution As Given Below I Find The Value Of Youtube
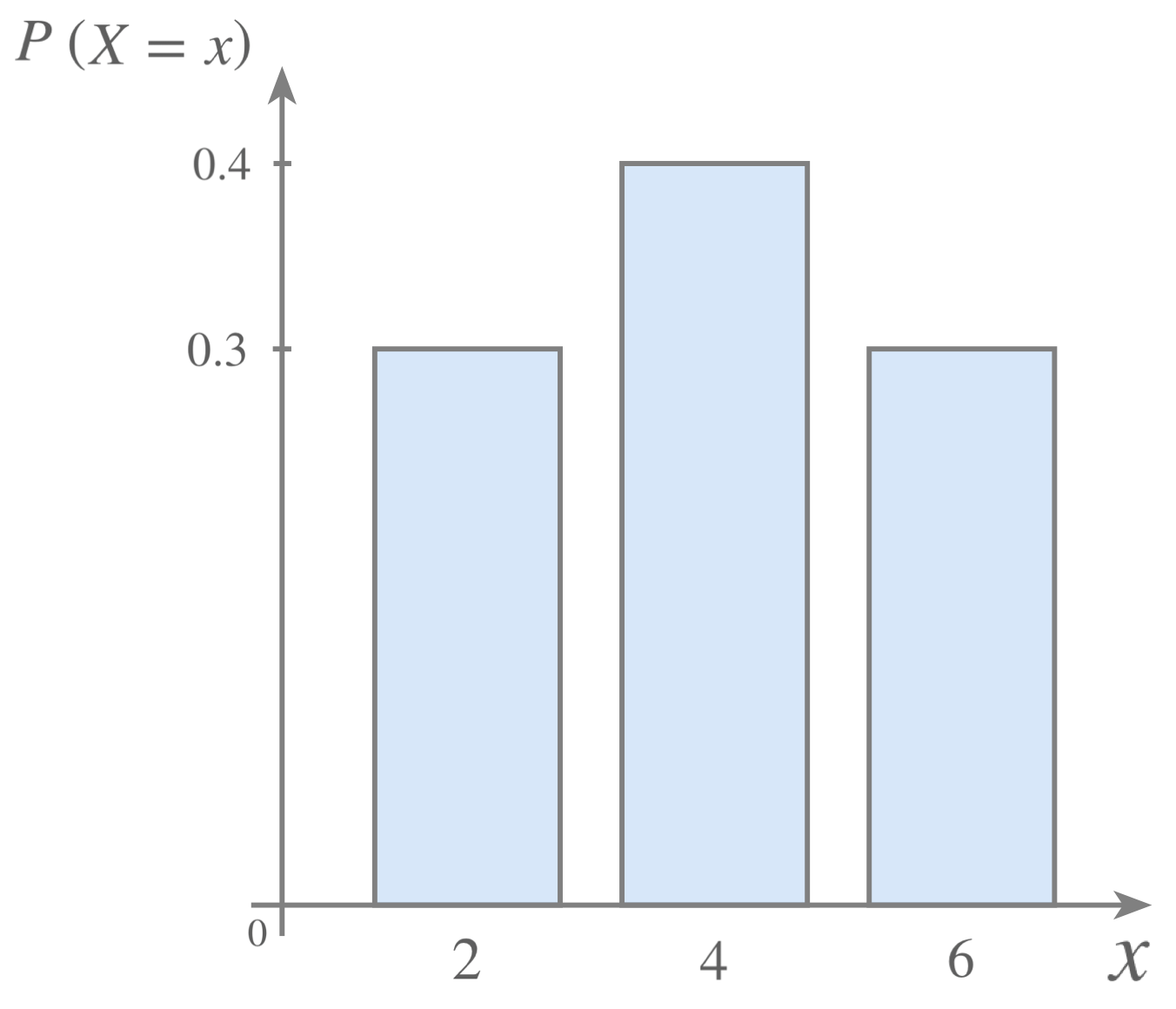
Discrete Random Variables Probability Distribution Functions

Normal Distribution Wikipedia

Pdf K Th Upper Record Values From Modified Weibull Distribution And Characterization
K Wiktionary

Variance Of Sum And Difference Of Random Variables Video Khan Academy

Determine The Value Of The Constant M So That The Function F X

Polynomial Conjecture Let W X Denote A Function Chegg Com

Tt Kp Free Font In Ttf Format For Free Download 30 98kb

Example 12 Show That F X X 1 If X Is Odd X 1 If X Is Even
F X 2x 2 16 4x 16 If X 2 At X 2 K If X 2 Studyrankersonline

Calculus Cheat Sheet Pauls Online Math Notes
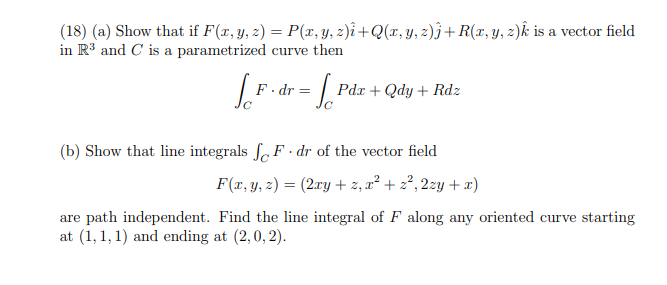
Solved 18 A Show That If F 1 Y Z P Y Z I Q X Chegg Com

The Random Variable X Has A Probability Distribution P X O

The Random Variable X Has A Probability Distribution P X O

Oneclass The Equilibrium Constant Kp For The Thermal Decomposition Of No2 Is 6 5 X 106 At 450a C 2no

What Is The Equation Of The Tangent To The Curve Y 3x 2 X 1 At Point 1 3 Quora

Pdf Probability Audrey Wu Academia Edu
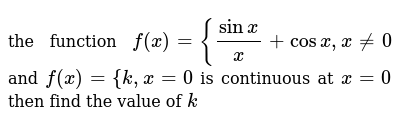
The Function F X Sinx X Cosx X 0 And F X K X 0 Is Con
Chapter 6 Joint Probability Distributions Probability And Bayesian Modeling

Appendix 1 Catalogue Of Texts In Medicine In Ancient Assur

Find The Values Of K So That The Function F Is Continuous At
Find The Values Of P And Q For Which F X 1 Sin 3 X 3cos 2 X If X Pi 2 And P If X Pi 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
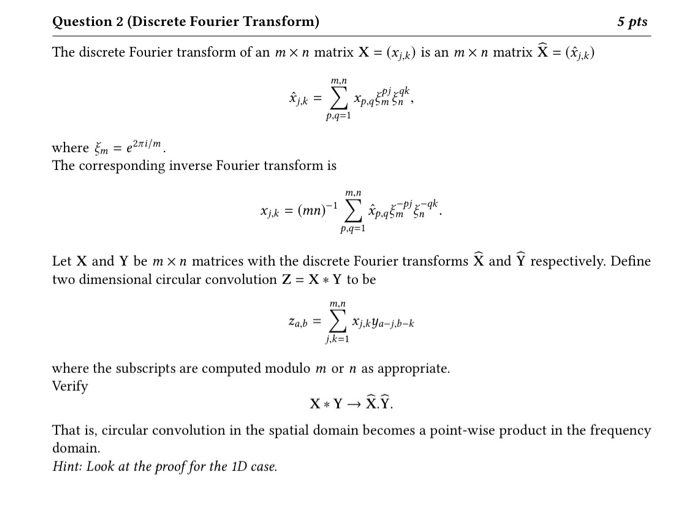
Solved Question 2 Discrete Fourier Transform 5 Pts The Chegg Com

7 1 The Central Limit Theorem For Sample Means Averages Introduction To Statistics

The Random Variable X Has A Probability Distribution P X O

Functions Continuous At Specific X Values Video Khan Academy
X Wiktionary
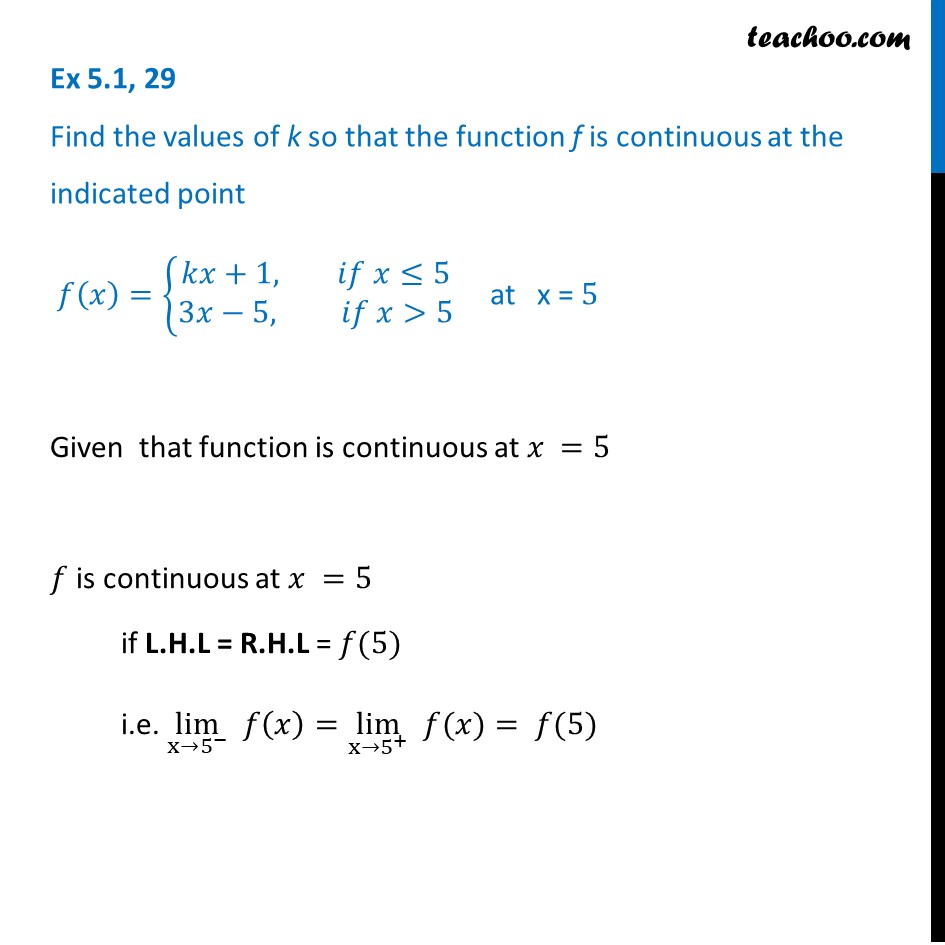
Ex 5 1 29 Find K F X Kx 1 3x 5 Is Continuous At X 5

The Random Variable X Has A Probability Distribution P X O

Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals

Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors

Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Exercise 8 6 Avail Pdf

Oneclass Please Help Me On These Equilibrium Questions I Am So Confused The Equilibrium Constant F

Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Exercise 8 6 Avail Pdf
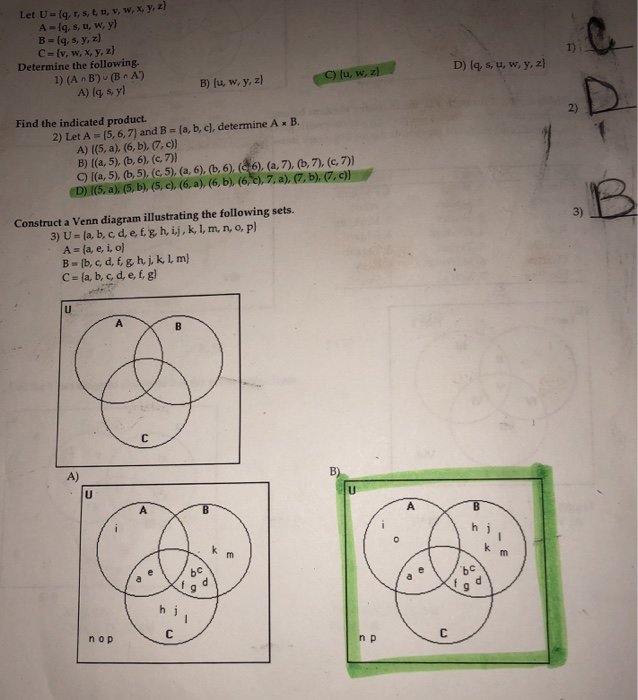
Solved Let U Q R S T U V W X Y Z A Q S U W Chegg Com

Txt 투모로우바이투게더 Logo Sticker By Kpop Corner In 21 Logo Sticker Print Stickers Kpop Logos

Marcinkiewicz Strong Laws For Linear Statistics Of Rho Mixing Sequences Of Random Variables

The Random Variable X Has A Probability Distribution P X O
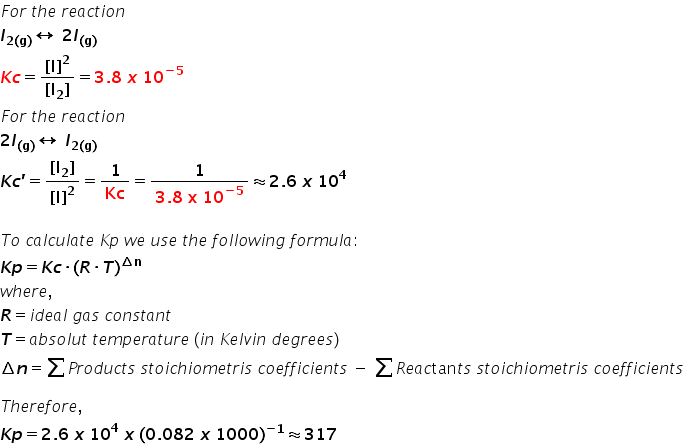
The Equilibrium Constant Kc For The Reaction I2 G 2i G Is 3 8 10 5 At 727 C Calculate Kc And Kp For The Equilibrium 2i G I2 G Homework Help And Answers Slader

Ex 5 1 28 Find K So That F X Kx 1 Cos X At X Pi

Data Structures And Algorithms Ppt Download

A Random Variable X Has The Following Probability Distribution

Solved Vectors Problems Iv Question1 Question2 Fon A T Chegg Com

Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors

Docslide Us 02 Formulae And Tables

Problem 1 5 Points Polynomial Conjecture Let Chegg Com

Write The Function In The Form F X X K Q X R Wyzant Ask An Expert

Python Stripping Accents On Strings Held In Lists Dic Learnprogramming
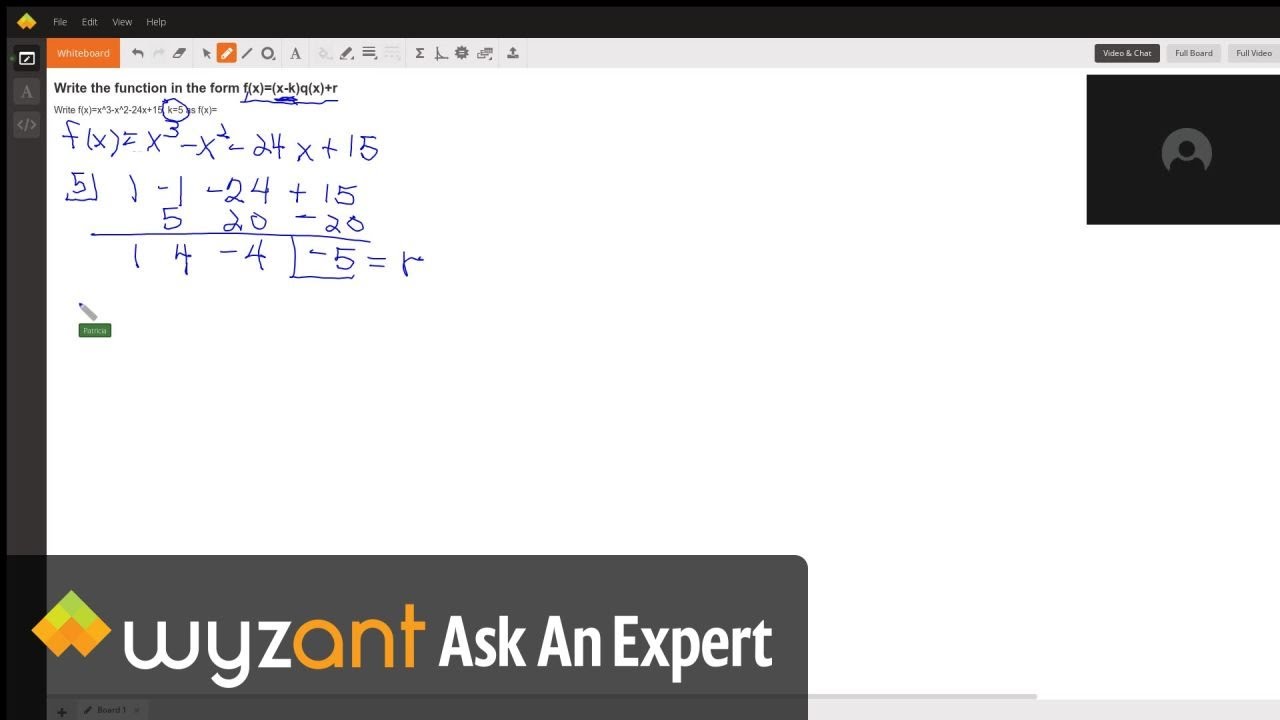
Write The Function In The Form F X X K Q X R Wyzant Ask An Expert
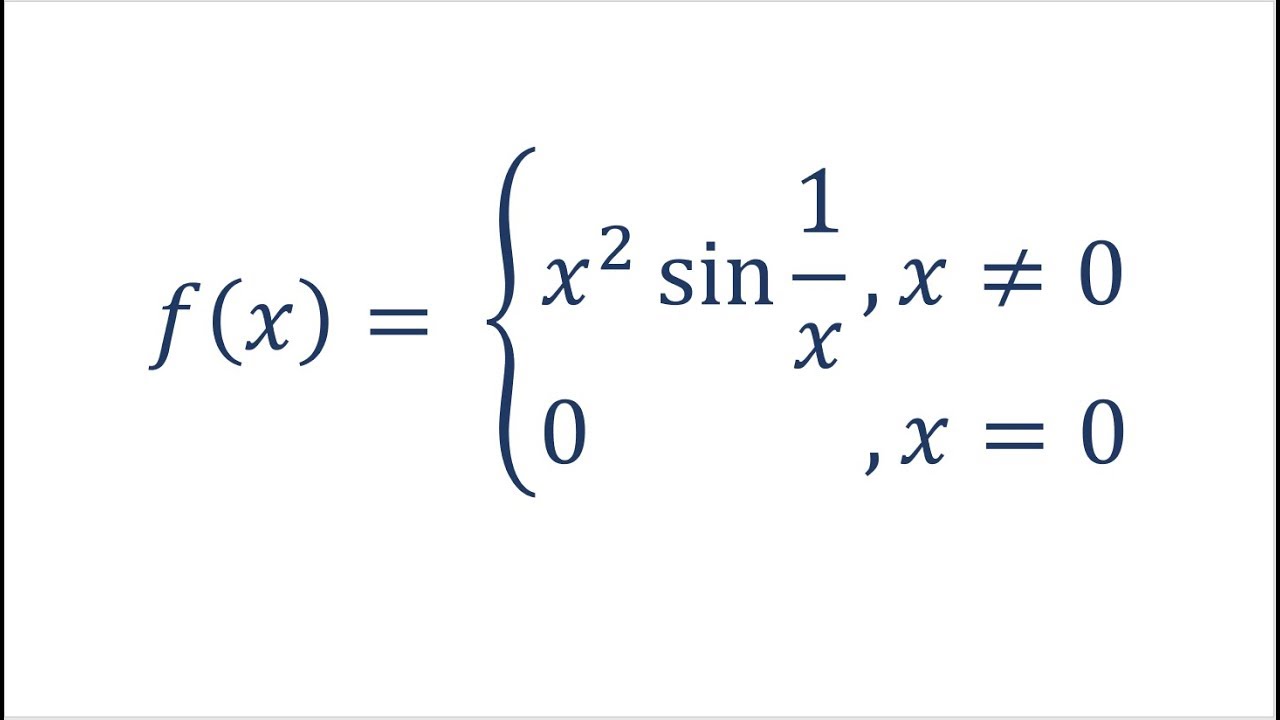
Does Derivative Have To Be Continuous Feat X 2sin 1 X Youtube

印刷 C Q 良い最高の壁紙無料thd
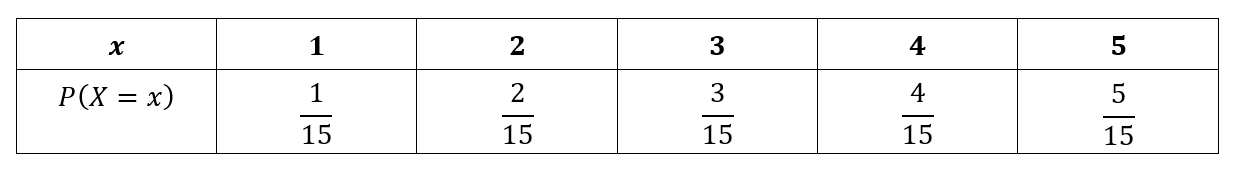
Discrete Random Variables Probability Distribution Functions

The Random Variable X Has A Probability Distribution P X O
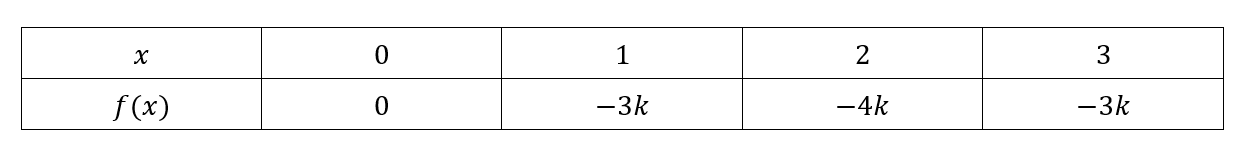
Discrete Random Variables Probability Distribution Functions

Use The Reduction Of Order Method To Solve The Following Problem Given One Of The Solution Y1 A X 2 1 Y 39 39 2xy 39 2y 0 Y1 X B 2x 1 Y 39 39 4 X 1 Y 39 4y 0 Y1 E 2x C X




