Vyux
X−y xy dxdy, where R is the triangular region with vertices (0,0), (1,0), (0,1) SOLUTION Here the region of integration is simple, but the function f(x,y) = cos x−y xy is not It seems reasonable to set u = x−y, v = xy Then, as the point (x,y) varies in R, the point (u,v) varies in the triangular region Q bounded by the lines u = v, v = 1, u = −v By the change of variables.

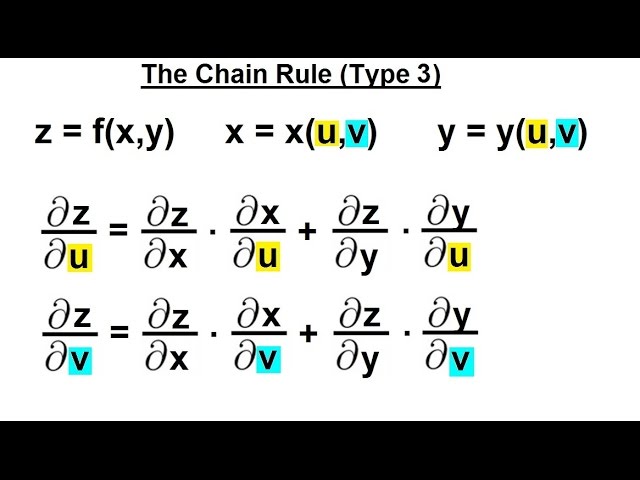
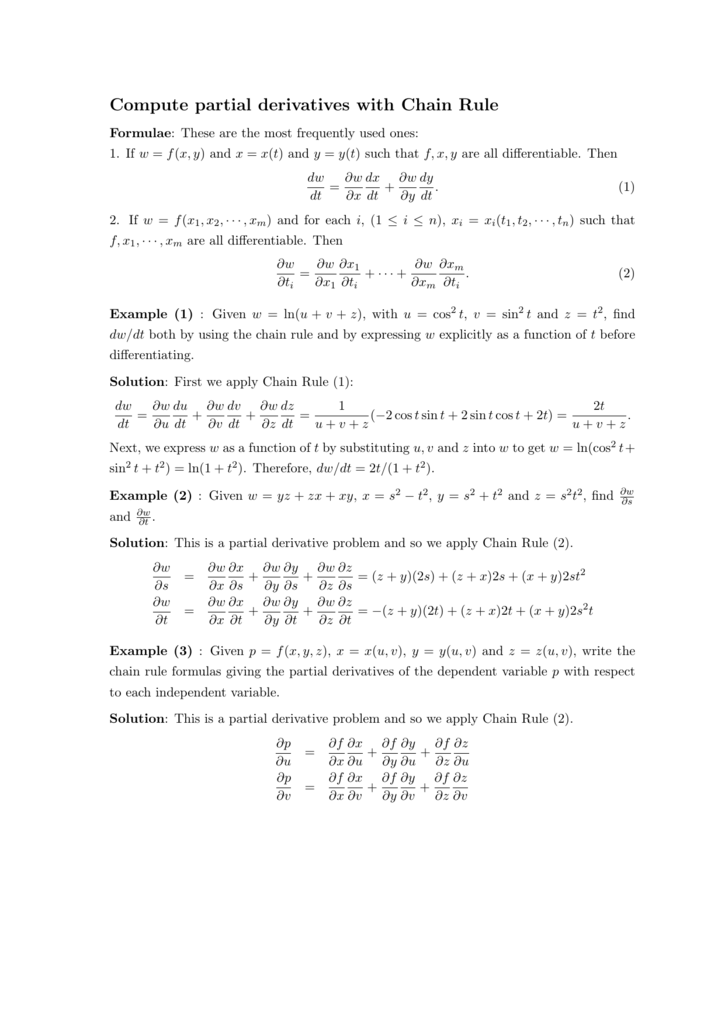
Vyux. Evaluate the surface integral {eq}\int \int_{S} (x y z) dS {/eq}, S is the parallelogram with parametric equations x = uv, y = uv, z = 12uv, {eq}0 \leq u. • Sometimes x and y are functions of one or more parameters We may find the derivative of a function with respect to that parameter using the chain rule • The formulas for calculating such derivatives are dz dt = @f @x dx dt @f @y dy dt and @z @t = @f @x @x @t @f @y @y @t • To calculate a partial derivative of a variable with respect to another requires im plicit. So that dw dt = 2yzt 3xz t2 (xy 2z)cost= 3sint.
Using the substitutions x = v x = v and y = u v, y = u v, evaluate the integral ∬ R y sin (y 2 − x) d A ∬ R y sin (y 2 − x) d A where R R is the region bounded by the lines y = x, x = 2, and y = 0 y = x, x = 2, and y = 0 Change of Variables for Triple Integrals Changing variables in triple integrals works in exactly the same way Cylindrical and spherical coordinate. Solution for Let x = u cos³ (v), y = u sin³ (v) (a) Sketch the region D in the xyplane corresponding to 1 < u < 3, T. 0 = (x 0,y 0) and f0(z 0) = u x(x 0,y 0)iv x(x 0,y 0) = v y(x 0,y 0)−iu y(x 0,y 0) Thus equating the real and imaginary parts we get u x = v y, u y = −v x, at z 0 = x 0 iy 0 (Cauchy Riemann equations) Proof Since f is differentiable at z 0 we have by varying h over the set of real numbers f 0(z 0) = f (x 0 iy 0) = lim h→0 u(x 0 h.
Ux = vy and ux = vy) ux = vy = 0 uy = vx and uy = vx) uy = vx = 0 Therefore ux = uy = 0so uis constant, and similarly vx = vy = 0so v is constant Hence f is constant as well 2 Determine the holomorphic functions f and g such that Ref = x2 y2 2y;. Plot the parametric surface x = u sin (v), y =u cos (v), z = v with different line styles for different values of v For 5 < v. Img = 2xy y Solution Let f = uiv Then, u = x2 y2 2y ) ux = 2x = vy) v = 2xy ˚(x) ) vx = 2y ˚0(x) = uy = 2y 2 ) ˚(x) = 2xc ) f = x2 y2 2y.
Question Use The Transformation T (u, V) (x(u, V), Y(u, V)) With X = 4 U V, Y = 4v U To Evaluate The Integral I = (x Y)dxdy When D Is The Square With Vertices (0,0), (1,4), (5,3) (4,1) Use The Transformation ( X,y) Y (u,v) With X = 4u, Y = 2v To Evaluate The Integral When R Is The Region Bounded By The Ellipse This problem has been solved!. Experts are waiting 24/7 to provide stepby. The derivative of tan − 1 (sin x cos x sin x − cos x ), with respect to 2 x , where (x ϵ (0, 2 π )) is Medium View solution Let f be a differential function such that f (x) = f (4 − x) and g (x) = f (2 x) for all x ∈ R, then This question has multiple correct options Hard View solution A curve has equation y = (2 x − 1) − 1 2 x x = 2 1 Find d x d y and d x 2 d 2 y.
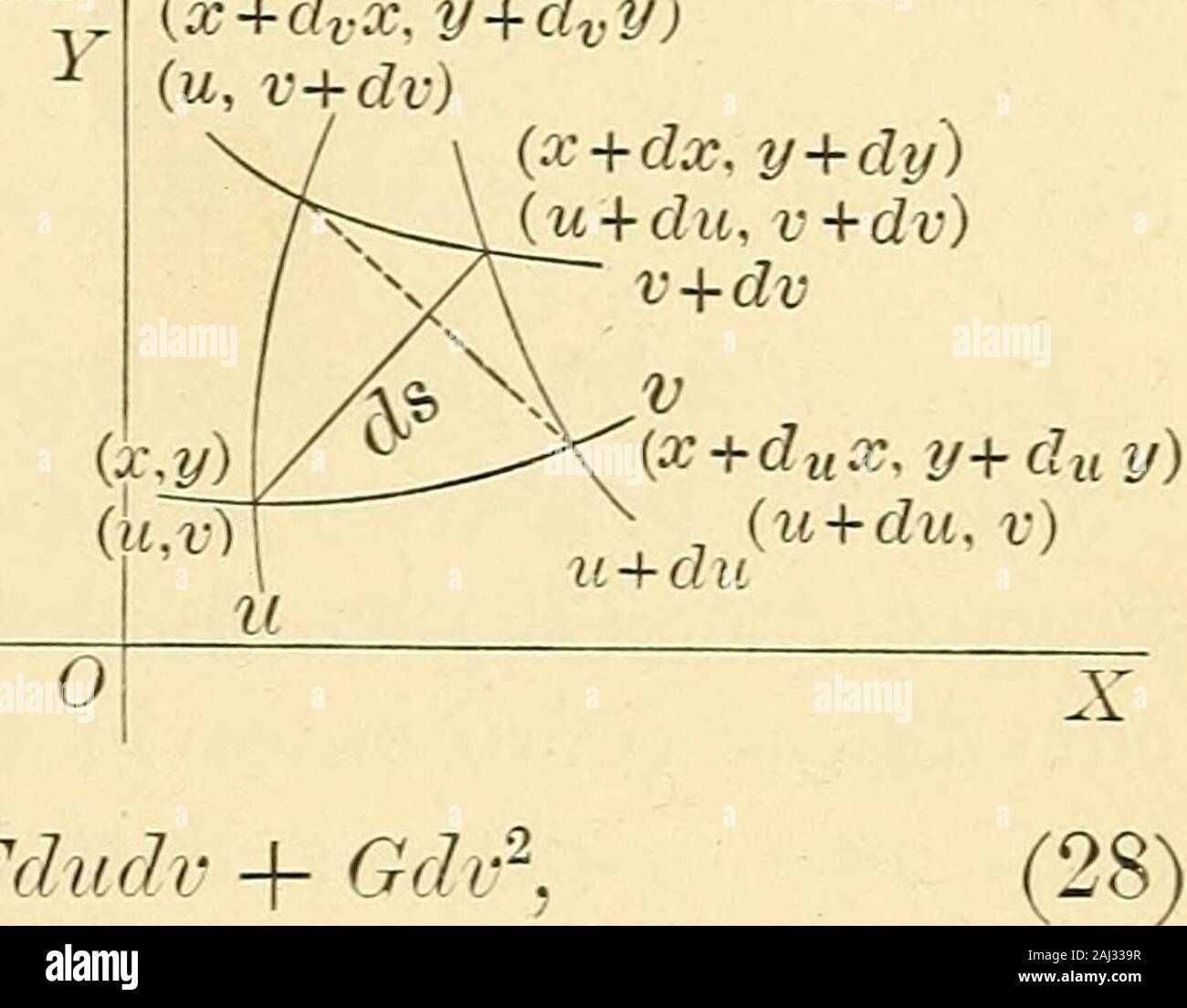
How to solve Use the chain rule to find the indicated derivative (partial g)/(partial u), where g (u, v) = f(x(u, v), y(u, v)), f(x, y) = 8x^2. ¶ 10 Let X be Hausdorff and locally compact, and view X as a subspace of its onepoint compactification X∗ Let f X → R be continuous Prove that f admits a continuous extension to X ∗(that is, there is F X → R continuous such that F(x) = f(x) for all x in X) if and only if for each > 0 there is a compact subset K. The Jacobian of x, yand zwith respect to u, vand w, denoted @(x;y;z) @(u;v;w) or J(u;v), is J(u;v) = @(x;y;z) @(u;v;w) = @z @x @u @x @v @x @w @y @u @v @w @u @z @v @w Example 354 Recall, when switching from Cartesian to polar coordinates, we have x= rcos and y= rsin The Jacobian of xand ywith respect to rand 44 CHANGE OF VARIABLE IN INTEGRALS THE JACOBIAN 233 is @(x;y) @(r;.
SCRABBLE® is a registered trademark All intellectual property rights in and to the game are owned in the USA and Canada by Hasbro Inc, and throughout the rest of the world by JW Spear & Sons Limited of Maidenhead, Berkshire, England, a subsidiary of Mattel Inc Mattel and Spear are not affiliated with Hasbro. X = 2u v, y = u 2v check_circle Expert Solution Want to see the full answer?. View 44docx from MATH MISC at Pakistan Degree College of Commerce for Boys, Allama Iqbal Town, Lahore If V y(uv) ,x and ,y x yy 445 a nth continued cf Exercise 430) If V ftmctlon Of (x.
X = u v, y = u − v, z = (u2 v2)/2, u2 v2 ≤ 16 Solution Let r(u,v) = (u v)i (u − v)j ((u2 v2)/2)k We have r u × r v = i j k 1 1 u 1 −1 v = (u v)i (u − v)j − 2k Hence, r u × r v = p (u v)2 (u − v)2 (−2)2 = 2u2 2v2 4 With Q = {(u,v) u2 v2 ≤ 16} we obtain A = ZZ Q r u × r vdA = ZZ Q p 2u2 2v2 4 dA = Z 2π 0 Z 4 0 p 2r2 4 rdrdθ = 2π h1 6. Surface 2 u;v ~r(u;v) = hx(u;v);y(u;v);z(u;v)i Examples 1If a surface is given by a formula z= f(x;y);it can be parametrized by taking xand yto be two parameters and considering the parametric equations x= x;. If X = U V , Y = U V Prove that J J , = 1 University of Mumbai BE Electrical Engineering Semester 1 (FE First Year) Question Papers 141 Important Solutions 527 Question Bank Solutions 529 Concept Notes 24 Time Tables 23 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads If X = U V , Y = U V Prove that J J , = 1 Applied Mathematics 1 If `x=uv, y=u/v"prove that" jj,=1` Advertisement.
26/05/ · In previous sections we’ve converted Cartesian coordinates in Polar, Cylindrical and Spherical coordinates In this section we will generalize this idea and discuss how we convert integrals in Cartesian coordinates into alternate coordinate systems Included will be a derivation of the dV conversion formula when converting to Spherical coordinates. Therefore, ∂v ∂y =∂u ∂x = U 0 π 4 y 0 1 x3 / 2 cos Å π 2 y 0 1 √ x ã Integrating wrt y, v = πU 0 0 4 x3 / 2 y cos Å π 2 y 0 1 √ x ã dy = U 0 y 2 x sin Å πy 0 2 √ x ã 0 1 U 0 π √ x cos Å πy 0 2 √ x ã f (x), where f is an arbitrary function of x. Dfxu, v, yu, v, u == dfduu, v Dfxu, v, yu, v, v == dfdvu, v which makes dfdu , dfdv equivalent to the partial derivatives with respect to u , v The output is a bit messy.
Wow, this merits a Scientific Explanation, about why u is a nonindependent entity, and a Brevitization for a More Complex Equational Persistency associable to. Let X,Y,Zbe independent,identically distributed (from now on,abbreviated iid) random variables,each with densityf(x)=6x5 for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1,and 0 elsewhere Find the distribution and density functions of the maximum of X,Yand Z 2 Let Xand Ybe independent,each with densitye−x,x≥ 0 Find the distribution (from now on,an abbreviation for “Find the distribution or density function”). For a parameterization, r(u,v) = hx(u,v),y(u,v),z(u,v)i We have r u = hx u,y u,z ui = a tangent vector to the surface in the udirection r v = hx v,y v,z vi = a tangent vector to the surface in the udirection We then get several facts 1 r u and r v together determine the tangent plane at a given point (because they are both ‘on’ this plane) So r u × r v would be a normal vector for.
Definition The Jacobian of the transformation $${\bf \Phi} (u,\,v) \ \longrightarrow \ (x(u,\, v), \, y(u, \,v))$$ is the $2\, \times\, 2$ determinant $$\frac. 01/10/ · In this section we will take a look at the basics of representing a surface with parametric equations We will also see how the parameterization of a surface can be used to find a normal vector for the surface (which will be very useful in a couple of sections) and how the parameterization can be used to find the surface area of a surface. Y= y z= 6 3x 2y Note that the given equation also implies that 2y= 6 3x zso that y= 3 3 2 x 1 2 zSo.
F(x;y)dxdy = ZZ D⁄ f(x(u;v);y(u;v)) fl fl fl fl @(x;y) @(u;v) fl fl fl fldudv We proved this for a linear map if f =1 when it says that the area of D is the area of D⁄ times the Jacobian determinant which is the determinant of the linear map The general case follows by dividing up D⁄ into smaller sets on which we can approximate. Let X˘ beta( ;. Partial derivative is a method for finding derivatives of multiple variables Get an idea on partial derivativesdefinition, rules and solved examples Learn More at BYJU’S.
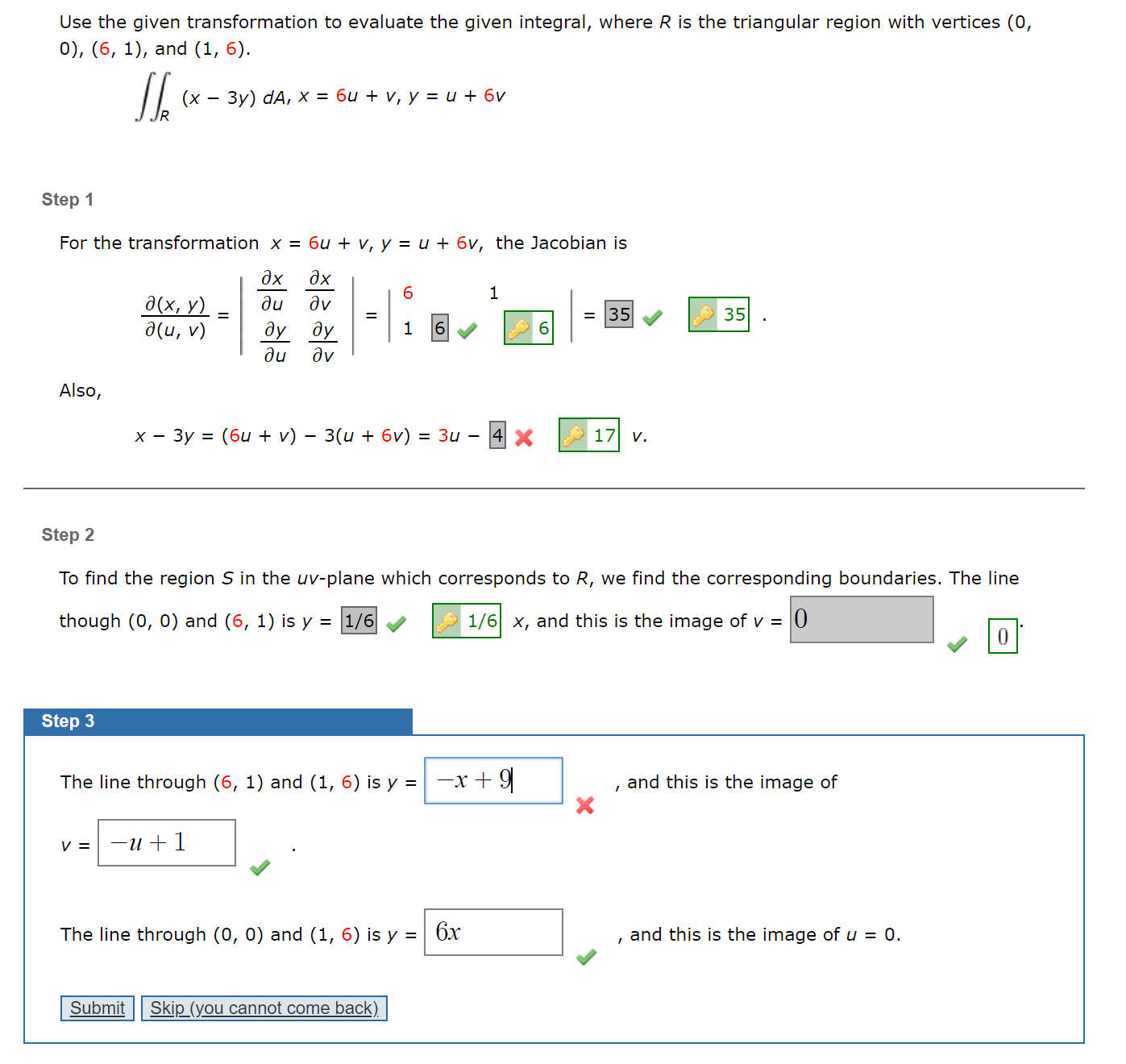
Terms of x and y instead of u and v, so () still ought to be needed, but sometimes one gets lucky The next example illustrates y Example 3 Evaluate dx dy, where R is the region pictured, having R x as boundaries the curves x2 −y2 = 1, x2 −y2 = 4, y = 0, y = x/2 Solution Since the boundaries of the region are contour curves of x2. 15 ∫∫ R (x – 3y) dA, where R is the triangular region with vertices (0, 0), (2, 1), and (1,2);. But avoid Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers.
Now I can ll in another part of the integral ZZ R (4x 8y)dA = Z 4 4 Z 8 0 (3u 5v) @(x;y) @(u;v) dvdu X (a) change R to S X (b) plug in u & v in place of x & y (c) calculate the Jacobian 3(c) The last ingredient I need for the change of variables is the Jacobian. Thanks for contributing an answer to Mathematics Stack Exchange!. Thereom $$\{x,y\}=\{u,v\} \rightarrow \biggx=u \wedge y=v \vee x=v \wedge y=u\bigg$$ Proof (by Contradiction) $$ \begin{align} (x \neq u \vee y\neq v)\wedge.
14/04/13 · Where S is the cone with parametric equations x = ucosv, y = usinv, z = u, 0. Set X = U V and Y = U − V Determine whether or not X and Y are independent 6 Let U and V be independent random variables, each uniformly distributed on 0,1 Determine the mean and variance of the random variable Y = 3U2−2V Second Practice First Midterm Exam 7 Consider the task of giving a 15– minute review lecture on the role of distri bution functions in probability. Y= y z= f(x;y) For example, the plane 3x 2y z= 6 can be parametrized as x= x;.
12/12/07 · Use the transformation x = 2u v, y = u 2v to evaluate the DOUBLE integral $$ x 3y dA, where R is the triangular region with vertices (0,0), (2,1), and (1,2) Notes $$ means double integral;. See the answer Double Integrals. Finding the jacobian is necessary (it equals 3).
E y X I y F S y D V y U P a ti nadie te valora B y F G y M N y H D y O J y A (siempre serán la mejor) R y M C y S L y Y J y A (Insisto, es la mejor) Perfect Couples J Y A E and X I and F S and D V y U P to you no one values you B and F G and M N and H D Y O J and A (always be the best) R Y M C and S L Y Y Y Y J and A (I insist, is the best) Translated English (US) Español;. V y u x v x u / is a tensor because (due to definition of tensor) > @ T v u y x u v y x » ¼ º « ¬ ª » » » » ¼ º « « « « ¬ ª w w w w » » » ¼ º « « « ¬ ª w w w w / T symbol for transpose of a vector, matrix So it can be easily shown that (1) 2 T H / Thus H, being the sum of two tensors, is also a tensor By using (1) it can be easily shown that H HT or that H. Use the transformation x = u − v, y = u v to set up the integral RR R (xy)dA in terms of u and v, where R is the region bounded by the lines, y = x, y = −x, y = 2 − x, and y = x − 4 Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Previous question Next question.
27/12/16 · If (x iy)3 = u iv, then show that u/x v/y = 4(x2 – y2) Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries. Suppose that x, yand zare functions of one variable t Then w= f(x;y;z) becomes a function of t Divide the equation above to get the derivative of f, df dt = f x dx dt f y dy dt f z dz dt This is an instance of the chain rule Example 111 Let f(x;y;z) = xyzz2 Suppose that x= t2, y= 3=t and z= sint Then f x= yz f y= xz and f z = 2z;. Check out a sample textbook solution See solution arrow_back Chapter 159, Problem 14E Chapter 159, Problem 16E arrow_forward Want to see this answer and more?.
30/04/18 · However, later we'll need to differentiate functions such as `y = sqrt(x^23x)(sin 4x^2)` (in the chapter Differentiation of Transcendental Functions) It is not possible to multiply this expression termbyterm, so we need a method to differentiate products of such functions. If u= u(x,y) and the two independent variables xand yare each a function of just one other variable tso that x= x(t) and y= y(t), then to finddu/dtwe write down the differential ofu δu= ∂u ∂x δx ∂u ∂y δy (1) Then taking limits δx→0, δy→0 and δt→0 in the usual way we have du dt = ∂u ∂x dx dt ∂u ∂y dy dt (2) Note we only need straight ‘d’s’ in dx/dtand. Please be sure to answer the questionProvide details and share your research!.
X xv yu yv , g(u,v) = f(x(u,v),y(u,v)), it looks as if the essential equations we need are the inverse equations () x = x(u,v), y = y(u,v) rather than the direct equations we are usually given (21) u = u(x,y), v = v(x,y) If it is awkward to get () by solving (21) simultaneously for x and y in terms of u and v, sometimes one can avoid having to do this by using the following relation. ) and Let Y ˘ beta( ;) If Xand Y are independent random variables nd the joint pdf of Uand V where U= XY and V = X EXERCISE 4 Suppose Yis the number of pollution particles in volume vand assume that Yfollows the Poisson distribution with mean v a If a point is randomly selected within the volume v nd the pdf of its. ) = @x @r @x.

Help In Proof Of Frac Partial U V Partial X Y Frac Partial X Y Partial U V 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Advanced Calculus Cations Of 60 Are That The Equations 22 Maythen Be Solved For X Y In Terms Of U V At Anypoint Of The Region And That There Is

If U And V Are Differential Function Of X And Y U V Then Prove That Dy Dx Dy Dx Dv Dx Brainly In
Vyux のギャラリー

Consider A Transformation Tu V Xu V Yu

If X I Y 3 U I V Then Show That U X V Y 4 X 2 Y 2

Consider A Transformation Tu V Xu V Yu
Calculus 3 Partial Derivative 28 Of 50 The Chain Rule Type 3 Youtube

Misc 16 If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Show That U X V Y

Displacement Field U X Y And V X Y Between An Initial Image And A Download Scientific Diagram
Compute Partial Derivatives With Chain Rule
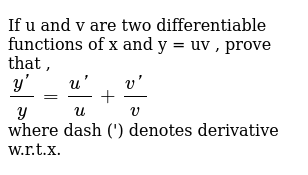
If U And V Are Two Differentiable Functions Of X And Y Uv Prov

14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts

Pin On Yu Boys Yugioh Arc V

Solve The Following Relations For X And Y And Compute The Jacobian J U V U X 4y V 3x 2y Homework Help And Answers Slader

Consider A Transformation T U V X U V Y U V From R 2 To R 2 Suppose T Is A Linear Transformation T U V Au Bv Cu Dv Then The Derivative Ppt
Answered Use The Given Transformation To Bartleby

If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Prove That U X V Y 4 X 2 Y 2 Brainly In

If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Show That U X V Y 4 X2 Y2 Here 2 And 3 Means Square Cube Respectively Brainly In

Derive The Jacobian Of U And V With Respect To X And Y Mathematics Stack Exchange
Basic Concepts

The Cauchy Riemann Equations Analytic Functions Coursera
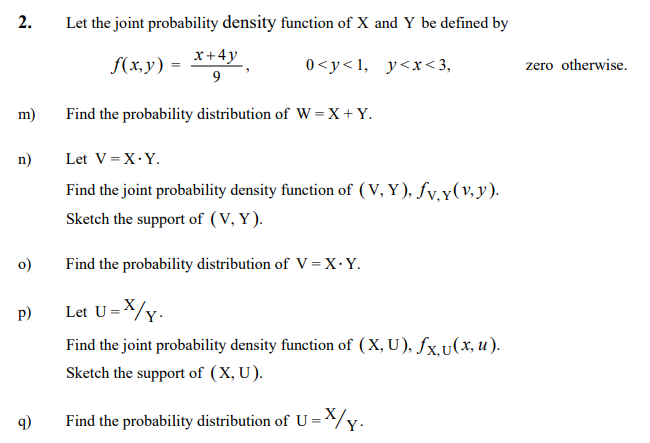
Solved 2 Let The Joint Probability Density Function Of X Chegg Com

If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Show That U X V Y 4 X 2 Y 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
9 4 How Does Divergence Relate To The Air Parcel S Area Change Meteo 300 Fundamentals Of Atmospheric Science

Introduction To Graph Algorithm Breadth First Search Algorithm In Python By Rashida Nasrin Sucky Towards Data Science

The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example 1 Page 152 Illustrates The Quotient Rule Reca

Oneclass Evaluate Dw Dv At U V 2 5 For Function W X Y Xy 2 Lnx X E U V Y Uv

The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example 1 Page 152 Illustrates The Quotient Rule Reca

Answered 2 A Solve The System U X 2y V Bartleby

Serena X Yuzu Yugioh Arc V Madebylizsenpai Yugioh Yu Gi Oh 5d S Anime
Keyboard Shortcut Ctrl U V Y W Z X Paste Sign Cut Sign Close Tab Sign Eps Ten Stock Illustration Illustration Of Home Fast
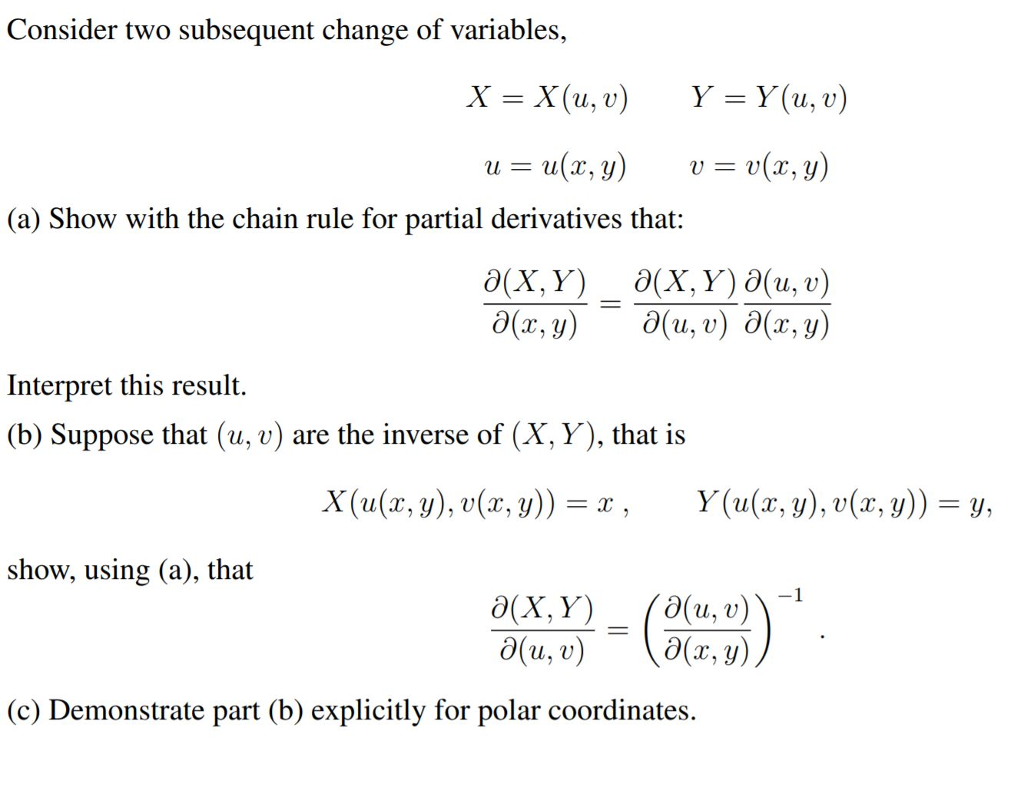
Solved Consider Two Subsequent Change Of Variables X X Chegg Com

Answered Change Of Variables Formula D H U Bartleby

Solved P F V W V X Y Z T W X Y Z T P Chegg Com

Consider A Transformation T U V X U V Y U V From R 2 To R 2 Suppose T Is A Linear Transformation T U V Au Bv Cu Dv Then The Derivative Ppt
Let U X And V X Satisfy The Differential Equations Du Dx P X U F X And Dv Dx P X V G X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

X U V And Y U V Find D X Y D U V Scholr

Obfuscated Hello World Program

U Unit3 Vm

14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts

Get Answer Help Anyone Please Solves This I Still Cant Figure It Out Why Transtutors

Solved For An Analytic Function F X Iy U X Y Iv X Y U Is Given By Self Study 365

Jacobian Properties Find ꝺ U V ꝺ R 8 When U X 2 Y 2 V 2xy X Rcos8 Y Rsin8 Youtube

If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Show That U X V Y 4 X2 Y2 Maths Complex Numbers And Quadratic Equations 1 Meritnation Com

2 Functional Dependence Differential Calculus Functions And Mappings

Jacobian Find ꝺ U V ꝺ R 8 If U 2xy V X 2 Y 2 Where X Rcos8 Y Rsin8 Youtube
Solved 27 30 Double Integrals Transformation Given To Evaluate The Fol Do Lowing Integrals Carry Out These Steps Sketch The Original Region Of Course Hero
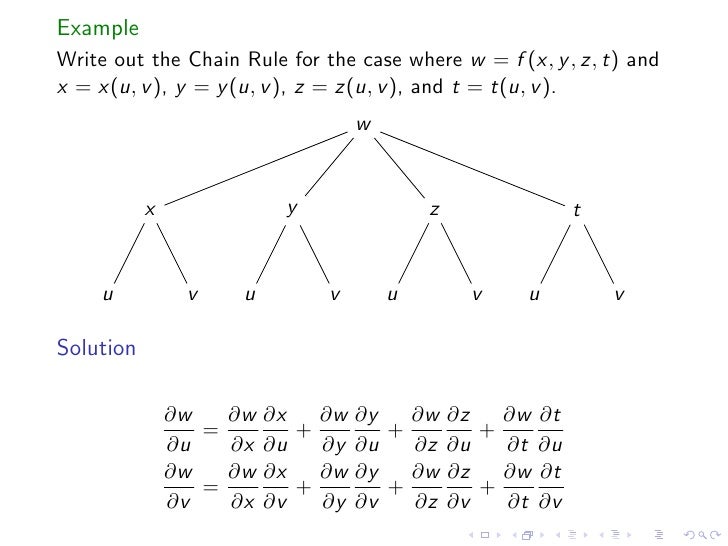
Lesson 23 The Chain Rule

Get Answer Help Anyone Please Solves This I Still Cant Figure It Out Why Transtutors

1 Vytah

Parametric Surfaces Chebfun

Fay S Trisecant Identity Wikipedia

Non Coordinate Time Velocity Pairs

Gec2 Tutorials Functions Of Several Variables

Verify Jj 1 Given X E U Cos V Y E U Sin V Mathematics Stack Exchange
How To Solve This Equation In Boolean Algebra X Y Z X Y U V Z U Quora

Find Dy Dx If Y U4 U 1 V V 5x2 2x 6 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com

Solved 1 Draw The Tree Diagram For The Chainrule And Wr Chegg Com
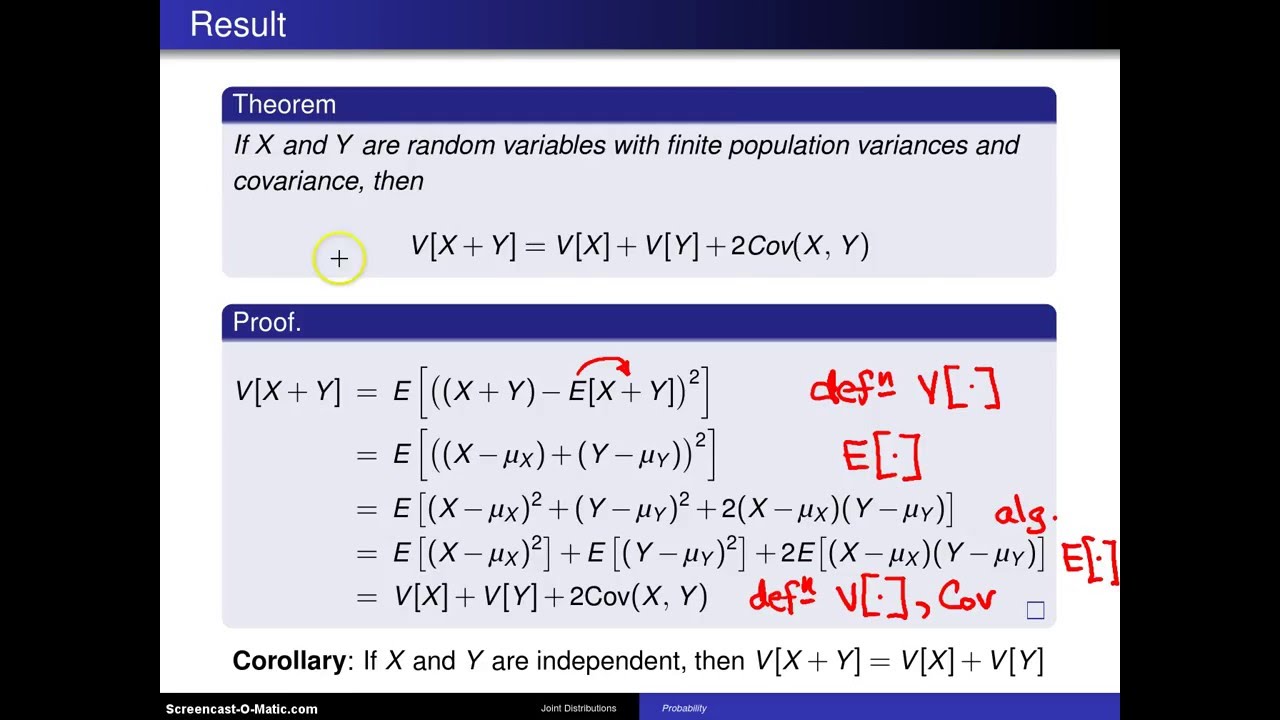
Covariance Result V X Y V X V Y 2 Cov X Y Youtube
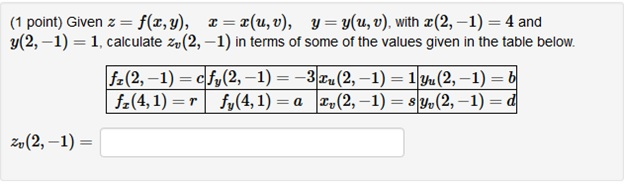
Solved Given Z F X Y X X U V Y Y U V With Chegg Com

Solved Please I Need Help With Both 27 And 28 No Need Fo Chegg Com
How To Solve This Equation X Y 3 Dx 3x Y 1 Dy 0 Quora

Ug Math

14 7 Change Of Variables In Multiple Integrals Jacobians Mathematics Libretexts

Misc 16 If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Show That U X V Y

Find F Z U X Y Iv X Y With U Or V As Given Check By The Cauchy Riemann Equations For Analyticity U Xy Homework Help And Answers Slader

Ux Vy Uy Vx If Ux Vy Uy
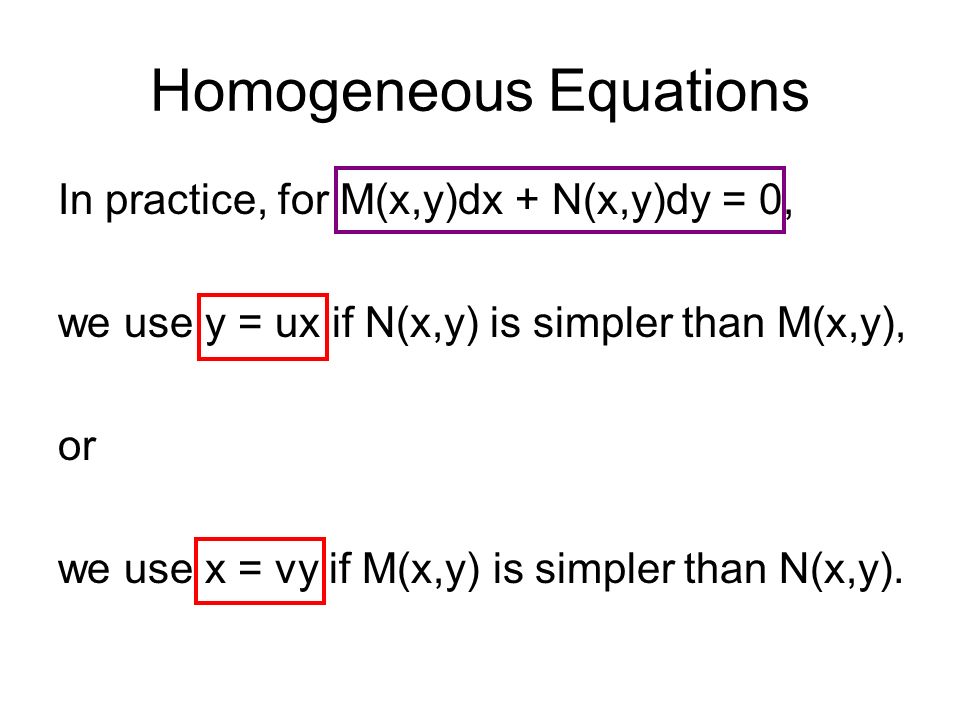
First Order Differential Equations Ppt Video Online Download

Find The Value For V X Y In The Function F X Iy U X Y Iv X Y With U X Y Log X 2 Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
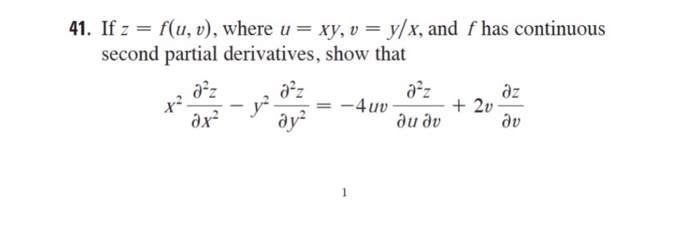
Solved If Z F U Y Where U Xy V Y X And F Has Co Chegg Com

Given Z F X Y X X U V Y Y U V With X 5 2 3 Y 5 2 1 Calculate Z U 5 2 In Terms Of Some Of The Values Given In The Table Below F X 5 2 A F Y 5 2 2 X U 5 2

2 Functional Dependence Differential Calculus Functions And Mappings




